Zero Latency Local First Apps with RxDB – Sync, Encryption and Compression
Creating a zero-latency local first application involves ensuring that most (if not all) user interactions occur instantaneously, without waiting on remote network responses. This design drastically enhances user experience, allowing apps to remain responsive and functional even when offline or experiencing poor connectivity. As developers, we can achieve this by storing data locally on the client and synchronizing it to the backend in the background. RxDB (Reactive Database) offers a comprehensive set of features - covering replication, offline support, encryption, compression, conflict handling, and more - that make it straightforward to build such high-performing apps.

Why Zero Latency with a Local First Approach?
In a traditional architecture, each user action triggers requests to a server for reads or writes. Despite network optimizations, unavoidable latencies can delay responses and disrupt the user flow. By contrast, a local first model maintains data in the client's environment (browser, mobile, desktop), drastically reducing user-perceived delays. Once the user re-connects or resumes activity online, changes propagate automatically to the server, eliminating manual synchronization overhead.
- Instant Responsiveness: Because user actions (queries, updates, etc.) happen against a local datastore, UI updates do not wait on round-trip times.
- Offline Operation: Apps can continue to read and write data, even when there is zero connectivity.
- Reduced Backend Load: Instead of flooding the server with small requests, replication can combine and push or pull changes in batches.
- Simplified Caching: Instead of implementing multi-layer caching, local first transforms your data layer into a reliable, quickly accessible store for all user actions.
RxDB: Your Key to Zero-Latency Local First Apps
RxDB is a JavaScript-based NoSQL database designed for offline-first and real-time replication scenarios. It supports a range of environments - browsers (IndexedDB or OPFS), mobile (Ionic, React Native), Electron, Node.js - and is built around:
- Reactive Queries that trigger UI updates upon data changes
- Schema-based NoSQL Documents for flexible but robust data models
- Advanced Sync Engine: to synchronize with diverse backends
- Encryption for secure data at rest
- Compression to reduce local and network overhead
Real-Time Sync and Offline-First
RxDB's replication logic revolves around pulling down remote changes and pushing up local modifications. It maintains a checkpoint-based mechanism, so only new or updated documents flow between the client and server, reducing bandwidth usage and latency. This ensures:
- Live Data: Queries automatically reflect server-side changes once they arrive locally.
- Background Updates: No manual polling needed; replication streams or intervals handle synchronization.
- Conflict Handling (see below) ensures data merges gracefully when multiple clients edit the same document offline.
Multiple Replication Plugins and Approaches
RxDB's flexible replication system lets you connect to different backends or even peer-to-peer networks. There are official plugins for CouchDB, Firestore, GraphQL, WebRTC, and more. Many developers create a custom HTTP replication to work with their existing REST-based backend, ensuring a painless integration that doesn't require adopting an entirely new server infrastructure.
Example Setup of a local database
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb/plugins/core';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
async function initZeroLocalDB() {
// Create a local RxDB instance using localstorage-based storage
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'myZeroLocalDB',
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage(),
// optional: password for encryption if needed
});
// Define one or more collections
await db.addCollections({
tasks: {
schema: {
title: 'task schema',
version: 0,
type: 'object',
primaryKey: 'id',
properties: {
id: { type: 'string', maxLength: 100 },
title: { type: 'string' },
done: { type: 'boolean' }
}
}
}
});
// Reactive query - automatically updates on local or remote changes
db.tasks
.find()
.$ // returns an RxJS Observable
.subscribe(allTasks => {
console.log('All tasks updated:', allTasks);
});
return db;
}When offline, reads and writes to db.tasks happen locally with near-zero delay. Once connectivity resumes, changes sync to the server automatically (if replication is configured).
Example Setup of the replication
import { replicateRxCollection } from 'rxdb/plugins/replication';
async function syncLocalTasks(db) {
replicateRxCollection({
collection: db.tasks,
replicationIdentifier: 'sync-tasks',
// Define how to pull server documents and push local documents
pull: {
handler: async (lastCheckpoint, batchSize) => {
// logic to retrieve updated tasks from the server since lastCheckpoint
},
},
push: {
handler: async (docs) => {
// logic to post local changes to the server
},
},
live: true, // continuously replicate
retryTime: 5000, // retry on errors or disconnections
});
}This replication seamlessly merges server-side and client-side changes. Your app remains responsive throughout, regardless of the network status.
Things you should also know about
Optimistic UI on Local Data Changes
A local first approach, especially with RxDB, naturally supports an optimistic UI pattern. Because writes occur on the client, you can instantly reflect changes in the interface as soon as the user performs an action - no need to wait for server confirmation. For example, when a user updates a task document to done: true, the UI can re-render immediately with that new state. This even works across multiple browser tabs.
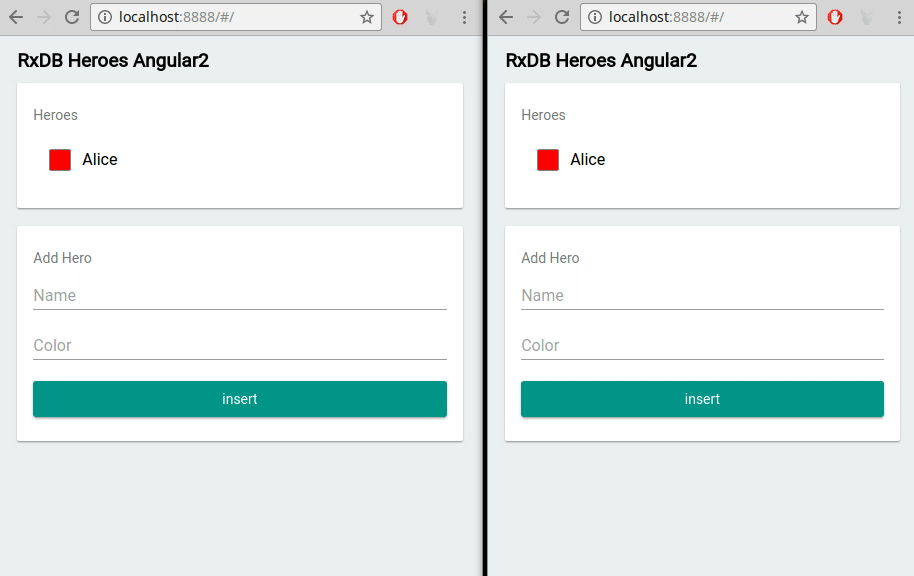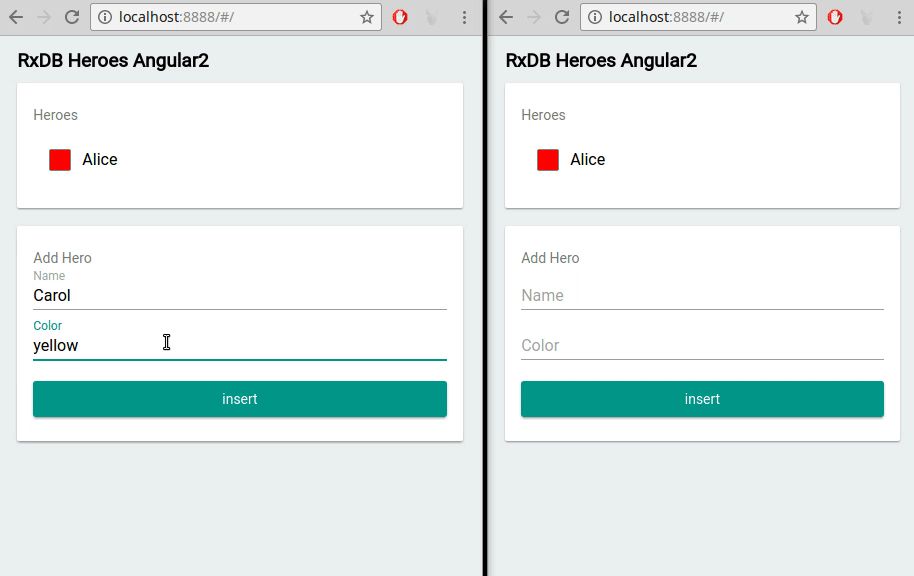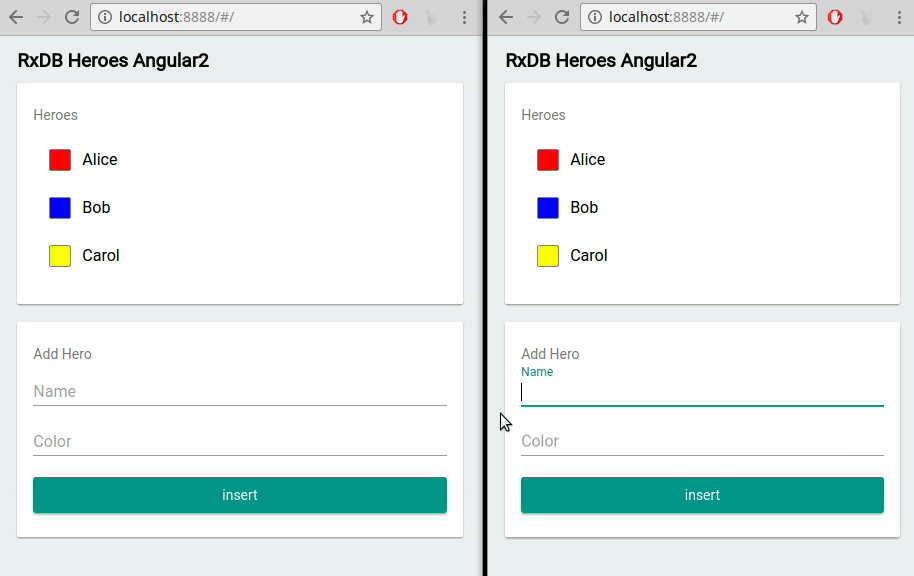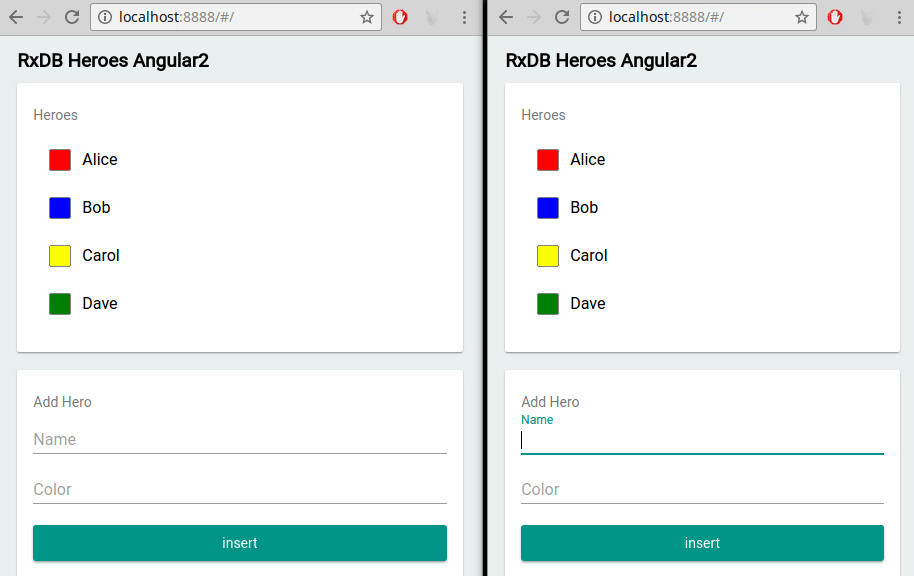
If a server conflict arises later during replication, RxDB's conflict handling logic determines which changes to keep, and the UI can be updated accordingly. This is far more efficient than blocking the user or displaying a spinner while the backend processes the request.
Conflict Handling
In local first models, conflicts emerge if multiple devices or clients edit the same document while offline. RxDB tracks document revisions so you can detect collisions and merge them effectively. By default, RxDB uses a last-write-wins approach, but developers can override it with a custom conflict handler. This provides fine-grained control - like merging partial fields, storing revision histories, or prompting users for resolution. Proper conflict handling keeps distributed data consistent across your entire system.
Schema Migrations
Over time, apps evolve - new fields, changed field types, or altered indexes. RxDB allows incremental schema migrations so you can upgrade a user's local data from one schema version to another. You might, for instance, rename a property or transform data formats. Once you define your migration strategy, RxDB automatically applies it upon app initialization, ensuring the local database's structure aligns with your latest codebase.
Advanced Features
Setup Encryption
When storing data locally, you may handle user-sensitive information like PII (Personal Identifiable Information) or financial details. RxDB supports on-device encryption to protect fields. For example, you can define:
import { wrappedKeyEncryptionCryptoJsStorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/encryption-crypto-js';
const encryptedStorage = wrappedKeyEncryptionCryptoJsStorage({
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage()
});
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'secureDB',
storage: encryptedStorage,
password: 'myEncryptionPassword'
});
await db.addCollections({
secrets: {
schema: {
title: 'secrets schema',
version: 0,
type: 'object',
primaryKey: 'id',
properties: {
id: { type: 'string', maxLength: 100 },
secretField: { type: 'string' }
},
required: ['id'],
encrypted: ['secretField'] // define which fields to encrypt
}
}
});Then mark fields as encrypted in the schema. This ensures data is unreadable on disk without the correct password.
Setup Compression
Local data can expand quickly, especially for large documents or repeated key names. RxDB's key compression feature replaces verbose field names with shorter tokens, decreasing storage usage and speeding up replication. You enable it by adding keyCompression: true to your collection schema:
await db.addCollections({
logs: {
schema: {
title: 'log schema',
version: 0,
keyCompression: true,
type: 'object',
primaryKey: 'id',
properties: {
id: { type: 'string'. maxLength: 100 },
message: { type: 'string' },
timestamp: { type: 'number' }
}
}
}
});Different RxDB Storages Depending on the Runtime
RxDB's storage layer is swappable, so you can pick the optimal adapter for each environment. Some common choices include:
- IndexedDB in modern browsers (default).
- OPFS (Origin Private File System) in browsers that support it for potentially better performance.
- SQLite for mobile or desktop environments via the premium plugin, offering native-like speed on Android, iOS, or Electron.
- In-Memory for tests or ephemeral data.
By choosing a suitable storage layer, you can adapt your zero-latency local first design to any runtime - web, mobile, or server-like contexts in Node.js.
Performance Considerations
Performant local data operations are crucial for a zero-latency experience. According to the RxDB storage performance overview, differences in underlying storages can significantly impact throughput and latency. For instance, IndexedDB typically performs well across modern browsers, OPFS offers improved throughput in supporting browsers, and SQLite storage (a premium plugin) often delivers near-native speed for mobile or desktop.
Offloading Work from the Main Thread
In a browser environment, you can move database operations into a Web Worker using the Worker RxStorage plugin. This approach lets you keep heavy data processing off the main thread, ensuring the UI remains smooth and responsive. Complex queries or large write operations no longer cause stuttering in the user interface.
Sharding or Memory-Mapped Storages
For large datasets or high concurrency, advanced techniques like sharding collections across multiple storages or leveraging a memory-mapped variant can further boost performance. By splitting data into smaller subsets or streaming it only as needed, you can scale to handle complex usage scenarios without compromising on the zero-latency user experience.
Follow Up
- Dive into the RxDB Quickstart to set up your own local first database.
- Explore Replication Plugins for syncing with platforms like CouchDB, Firestore, or GraphQL.
- Check out Advanced Conflict Handling and Performance Tuning for big data sets or complex multi-user interactions.
- Join the RxDB Community on GitHub and Discord to share insights, file issues, and learn from other developers building zero-latency solutions.
By integrating RxDB into your stack, you achieve millisecond interactions, full offline capabilities, secure data at rest, and minimal overhead for large or distributed teams. This zero-latency local first architecture is the future of modern software - delivering a fluid, always-available user experience without overcomplicating the developer workflow.
 Ask a question on the forums about Zero Latency Local...
Ask a question on the forums about Zero Latency Local...