SQLite RxStorage
This RxStorage is based on SQLite and is made to work with Node.js, Electron, React Native and Capacitor or SQLite via webassembly in the browser. It can be used with different so called sqliteBasics adapters to account for the differences in the various SQLite bundles and libraries that exist.
SQLite is a natural fit for RxDB because most platforms - Android, iOS, Node.js, and beyond - already ship with a built-in SQLite engine, delivering robust performance and minimal setup overhead. Its proven reliability, having powered countless applications over the years, ensures a battle-tested foundation for local data. By placing RxDB on top of SQLite, you gain advanced features suited for building interactive, offline-capable UI apps: real-time queries, reactive state updates, conflict handling, data encryption, and straightforward schema management. This combination offers a unified NoSQL-like experience without sacrificing the speed and broad availability that SQLite brings.
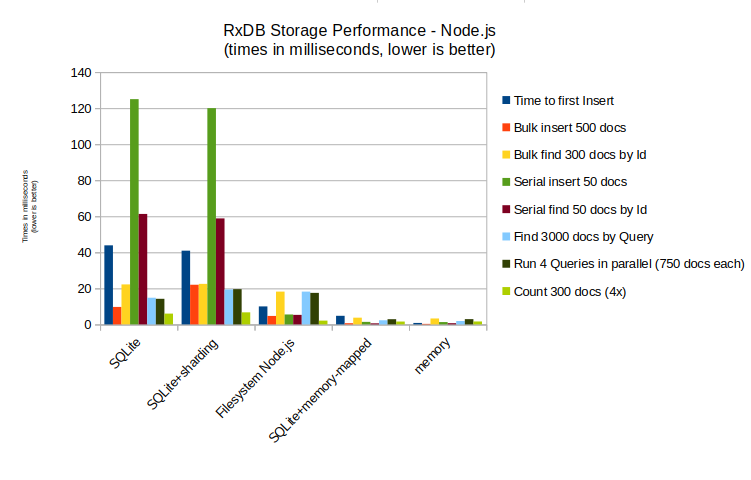
Performance comparison with other storages
The SQLite storage is a bit slower compared to other Node.js based storages like the Filesystem Storage because wrapping SQLite has a bit of overhead and sending data from the JavaScript process to SQLite and backwards increases the latency. However for most hybrid apps the SQLite storage is the best option because it can leverage the SQLite version that comes already installed on the smartphone's OS (iOS and android). Also for desktop Electron apps it can be a viable solution because it is easy to ship SQLite together inside of the Electron bundle.
Using the SQLite RxStorage
There are two versions of the SQLite storage available for RxDB:
-
The trial version which comes directly shipped with RxDB Core. It contains an SQLite storage that allows you to try out RxDB on devices that support SQLite, like React Native or Electron. While the trial version does pass the full RxDB storage test-suite, it is not made for production. It is not using indexes, has no attachment support, is limited to store 300 documents and fetches the whole storage state to run queries in memory. Use it for evaluation and prototypes only!
-
The RxDB Premium 👑 version which contains the full production-ready SQLite storage. It contains a full load of performance optimizations and full query support. To use the SQLite storage you have to import
getRxStorageSQLitefrom the RxDB Premium 👑 package and then add the correctsqliteBasicsadapter depending on which sqlite module you want to use. This can then be used as storage when creating the RxDatabase. In the following you can see some examples for some of the most common SQLite packages.
// Import the Trial SQLite Storage
import {
getRxStorageSQLiteTrial,
getSQLiteBasicsNodeNative
} from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-sqlite';
// Create a Storage for it, here we use the nodejs-native SQLite module
// other SQLite modules can be used with a different sqliteBasics adapter
import { DatabaseSync } from 'node:sqlite';
const storage = getRxStorageSQLiteTrial({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsNodeNative(DatabaseSync)
});
// Create a Database with the Storage
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: storage
});In the following, all examples are shown with the premium SQLite storage. Still they work the same with the trial version.
SQLiteBasics
Different SQLite libraries have different APIs to create and access the SQLite database. Therefore the library must be massaged to work with the RxDB SQlite storage. This is done in a so-called SQLiteBasics interface. RxDB directly ships with a wide range of these for various SQLite libraries that are commonly used. Also creating your own one is pretty simple, check the source code of the existing ones for that.
For example for the sqlite3 npm library we have the getSQLiteBasicsNode() implementation. For node:sqlite we have the getSQLiteBasicsNodeNative() implementation and so on..
Using the SQLite RxStorage with different SQLite libraries
Usage with the sqlite3 npm package
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsNode
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
/**
* In Node.js, we use the SQLite database
* from the 'sqlite' npm module.
* @link https://www.npmjs.com/package/sqlite3
*/
import sqlite3 from 'sqlite3';
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
/**
* Different runtimes have different interfaces to SQLite.
* For example in node.js we have a callback API,
* while in capacitor sqlite we have Promises.
* So we need a helper object that is capable of doing the basic
* sqlite operations.
*/
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsNode(sqlite3)
})
});Usage with the node:sqlite package
With Node.js version 22 and newer, you can use the "native" sqlite module that comes shipped with Node.js.
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsNodeNative
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import { DatabaseSync } from 'node:sqlite';
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsNodeNative(DatabaseSync)
})
});Usage with Webassembly in the Browser
In the browser you can use the wa-sqlite package to run SQLite in Webassembly. The wa-sqlite module also allows using persistence with IndexedDB or OPFS. Notice that in general SQLite via Webassembly is slower compared to other storages like IndexedDB or OPFS because sending data from the main thread to wasm and backwards is slow in the browser. Have a look at the performance comparison.
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsWasm
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
/**
* In the Browser, we use the SQLite database
* from the 'wa-sqlite' npm module. This contains the SQLite library
* compiled to Webassembly
* @link https://www.npmjs.com/package/wa-sqlite
*/
import SQLiteESMFactory from 'wa-sqlite/dist/wa-sqlite-async.mjs';
import SQLite from 'wa-sqlite';
const sqliteModule = await SQLiteESMFactory();
const sqlite3 = SQLite.Factory(module);
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsWasm(sqlite3)
})
});Usage with React Native
- Install the react-native-quick-sqlite npm module
- Import
getSQLiteBasicsQuickSQLitefrom the SQLite plugin and use it to create a RxDatabase:
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsQuickSQLite
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import { open } from 'react-native-quick-sqlite';
// create database
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
multiInstance: false, // <- Set multiInstance to false when using RxDB in React Native
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsQuickSQLite(open)
})
});If react-native-quick-sqlite does not work for you, as alternative you can use the react-native-sqlite-2 library instead:
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsWebSQL
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import SQLite from 'react-native-sqlite-2';
const storage = getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsWebSQL(SQLite.openDatabase)
});Usage with Expo SQLite
Notice that expo-sqlite cannot be used on android (but it works on iOS) if you use Expo SDK version 50 or older. Please update to Version 50 or newer to use it.
In the latest expo SDK version, use the getSQLiteBasicsExpoSQLiteAsync() method:
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsExpoSQLiteAsync
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import * as SQLite from 'expo-sqlite';
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
multiInstance: false,
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsExpoSQLiteAsync(SQLite.openDatabaseAsync)
})
});In older Expo SDK versions, you might have to use the non-async API:
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsExpoSQLite
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import { openDatabase } from 'expo-sqlite';
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
multiInstance: false,
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsExpoSQLite(openDatabase)
})
});Usage with SQLite Capacitor
- Install the sqlite capacitor npm module
- Add the iOS database location to your capacitor config
{
"plugins": {
"CapacitorSQLite": {
"iosDatabaseLocation": "Library/CapacitorDatabase"
}
}
}- Use the function
getSQLiteBasicsCapacitorto get the capacitor sqlite wrapper.
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsCapacitor
} from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite';
/**
* Import SQLite from the capacitor plugin.
*/
import {
CapacitorSQLite,
SQLiteConnection
} from '@capacitor-community/sqlite';
import { Capacitor } from '@capacitor/core';
const sqlite = new SQLiteConnection(CapacitorSQLite);
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
/**
* Different runtimes have different interfaces to SQLite.
* For example in node.js we have a callback API,
* while in capacitor sqlite we have Promises.
* So we need a helper object that is capable of doing the basic
* sqlite operations.
*/
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsCapacitor(sqlite, Capacitor)
})
});Usage with Tauri SQLite
- Add the Tauri SQL plugin to your Tauri project.
- Make sure to add
sqliteas your database engine by runningcargo add tauri-plugin-sql --features sqliteinsidesrc-tauri. - Use the
getSQLiteBasicsTaurifunction to get the Tauri SQLite wrapper.
import {
createRxDatabase
} from 'rxdb';
import {
getRxStorageSQLite,
getSQLiteBasicsTauri
} from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-sqlite';
import sqlite3 from '@tauri-apps/plugin-sql';
const myRxDatabase = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'exampledb',
storage: getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsTauri(sqlite3)
})
});Database Connection
If you need to access the database connection for any reason you can use getDatabaseConnection to do so:
import { getDatabaseConnection } from 'rxdb-premium/plugins/storage-sqlite'It has the following signature:
getDatabaseConnection(
sqliteBasics: SQLiteBasics<any>,
databaseName: string
): Promise<SQLiteDatabaseClass>;Known Problems of SQLite in JavaScript apps
-
Some JavaScript runtimes do not contain a
BufferAPI which is used by SQLite to store binary attachments data asBLOB. You can setstoreAttachmentsAsBase64String: trueif you want to store the attachments data as base64 string instead. This increases the database size but makes it work even without having aBuffer. -
The SQlite RxStorage works on SQLite libraries that use SQLite in version
3.38.0 (2022-02-22)or newer, because it uses the SQLite JSON methods likeJSON_EXTRACT. If you get an error like[Error: no such function: JSON_EXTRACT (code 1 SQLITE_ERROR[1]), you might have a too old version of SQLite. -
To debug all SQL operations, you can pass a log function to
getRxStorageSQLite()like this. This does not work with the trial version:
const storage = getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsCapacitor(sqlite, Capacitor),
// pass log function
log: console.log.bind(console)
});- By default, all tables will be created with the
WITHOUT ROWIDflag. Some tools like drizzle do not support tables with that option. You can disable it by settingwithoutRowId: falsewhen callinggetRxStorageSQLite():
const storage = getRxStorageSQLite({
sqliteBasics: getSQLiteBasicsCapacitor(sqlite, Capacitor),
withoutRowId: false
}); Ask a question on the forums about SQLite RxStorage
Ask a question on the forums about SQLite RxStorage