RxDB as a Database in a Vue Application
In the modern web ecosystem, Vue has become a leading choice for building highly performant, reactive single-page applications (SPAs). However, while Vue excels at managing and updating the user interface, robust and efficient data handling also plays a pivotal role in delivering a great user experience. Enter RxDB, a reactive JavaScript database that runs in the browser (and beyond), offering significant capabilities such as offline-first data handling, real-time synchronization, and straightforward integration with Vue's reactivity system.
This article explores how RxDB works, why it's a perfect match for Vue, and how you can leverage it to build more engaging, performant, and data-resilient Vue applications.
Why Vue Applications Need a Database
Vue is renowned for its lightweight core and flexible architecture centered around reactive state management and reusable components. However, modern Vue applications often require:
- Offline Capabilities: Allowing users to continue working even without internet access.
- Real-Time Updates: Keeping UI data in sync with changes as they occur, whether locally or from other connected clients.
- Improved Performance: Reducing server round trips and leveraging local storage for faster data operations.
- Scalable Data Handling: Managing increasingly large datasets or complex queries right in the browser.
While you can store data in Vuex/Pinia stores or via direct AJAX calls, these solutions may not suffice when your application demands a full-featured offline-first database or complex synchronization with a server. RxDB addresses these needs with a dedicated, reactive, browser-based database that pairs seamlessly with Vue's reactivity system.
Introducing RxDB as a Database Solution
RxDB - short for Reactive Database - is built on the principle of combining NoSQL database capabilities with reactive programming. It runs inside your client-side environment (browser, Node.js, or mobile devices) and provides:
- Real-Time Reactivity: Automatically updates subscribed components whenever data changes.
- Offline-First Approach: Stores data locally and syncs with the server when online connectivity is restored.
- Data Replication: Effortlessly keeps data synchronized across multiple tabs, devices, or server instances.
- Multi-Tab Support: Seamlessly propagates changes to all open tabs in the user's browser.
- Observable Queries: Automatically refresh the result set when documents in your queried collection change.
RxDB vs. Other Vue Database Options
Compared to traditional approaches - like raw IndexedDB or local storage - RxDB adds a powerful, reactive layer that simplifies your data flow. While tools like Vuex or Pinia are great for state management, they are not fully fledged databases with features like replication, conflict resolution, and offline persistence. RxDB bridges the gap by providing an integrated data handling solution tailor-made for modern, data-intensive Vue applications.
Getting Started with RxDB
Let's break down the essentials for using RxDB within a Vue application.
Installation
You can install RxDB (and RxJS, which it depends on) via npm or yarn:
npm install rxdb rxjsCreating and Configuring Your Database
Within your Vue project, you can set up an RxDB instance in a dedicated file or a Vue plugin. Below is an example using Localstorage as the storage engine:
// db.js
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
export async function initDatabase() {
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'heroesdb',
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage(),
password: 'myPassword', // optional encryption password
multiInstance: true, // multi-tab support
eventReduce: true // optimize event handling
});
await db.addCollections({
hero: {
schema: {
title: 'hero schema',
version: 0,
primaryKey: 'id',
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: { type: 'string' },
name: { type: 'string' },
healthpoints: { type: 'number' }
}
}
}
});
return db;
}After creating the RxDB instance, you can share it across your application (for example, by providing it in a plugin or a global property in Vue).
Vue Reactivity and RxDB Observables
RxDB queries return RxJS observables (.$). Vue can automatically update components when data changes if you manually subscribe and store results in Vue refs/reactive objects, or if you use RxDB's custom reactivity for Vue.
Example with Vue 3 Composition API:
// HeroList.vue
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue';
import { initDatabase } from '@/db';
const heroes = ref([]);
let db;
onMounted(async () => {
db = await initDatabase();
// Subscribe to an RxDB query
db.hero
.find({
selector: {
healthpoints: { $gt: 0 }
},
sort: [{ name: 'asc' }]
})
.$ // the dot-$ is an observable that emits whenever the query results change
.subscribe((newHeroes) => {
heroes.value = newHeroes;
});
});
</script>
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="hero in heroes" :key="hero.id">
{{ hero.name }} - HP: {{ hero.healthpoints }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>Different RxStorage Layers for RxDB
RxDB supports multiple storage backends - called "RxStorage layers" - giving you flexibility in how data is persisted:
- LocalStorage RxStorage: Uses the browsers localstorage API.
- IndexedDB RxStorage: Direct usage of native IndexedDB.
- OPFS RxStorage: Uses the File System Access API for even faster storage in modern browsers.
- Memory RxStorage: Stores data in memory, ideal for tests or ephemeral data.
- SQLite RxStorage: Runs SQLite, which can be compiled to WebAssembly for the browser. While possible, it typically carries a larger bundle size compared to native browser APIs like IndexedDB or OPFS.
Choose the storage option that best aligns with your Vue application's requirements for performance, persistence, and platform compatibility.
Synchronizing Data with RxDB between Clients and Servers
RxDB champions an offline-first approach: data is kept locally so that your Vue app remains usable, even without internet. When connectivity is restored, RxDB ensures your local changes synchronize to the server, resolving conflicts as necessary.
- Real-Time Synchronization: With RxDB's replication plugins, any local change can be instantly pushed to a remote endpoint while pulling down remote changes to ensure consistency.
- Conflict Resolution: In multi-user scenarios, conflicts may arise if two clients update the same document simultaneously. RxDB provides hooks to handle and resolve these gracefully.
- Scalable Architecture: By reducing reliance on continuous server requests, you can lighten server load and deliver a more responsive user experience.
Advanced RxDB Features and Techniques
Offline-First Approach
Vue applications can seamlessly function offline by leveraging RxDB's local database storage. The moment the network is restored, all unsynced data is pushed to the server. This capability is particularly beneficial for Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and scenarios with spotty connectivity.
Observable Queries and Change Streams
Beyond simply returning data, RxDB queries emit observables that respond to any change in the underlying documents. This real-time approach can drastically simplify state management, since updates flow directly into your Vue components without additional manual wiring.
Encryption of Local Data
For applications handling sensitive information, RxDB supports encryption of local data. Your data is stored securely in the browser, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Indexing and Performance Optimization
By defining indexes on frequently searched fields, you can speed up queries and reduce overall resource usage. This is crucial for larger datasets where performance might otherwise degrade.
JSON Key Compression
This optimization shortens field names in stored JSON documents, thereby reducing storage space and potentially improving performance for read/write operations.
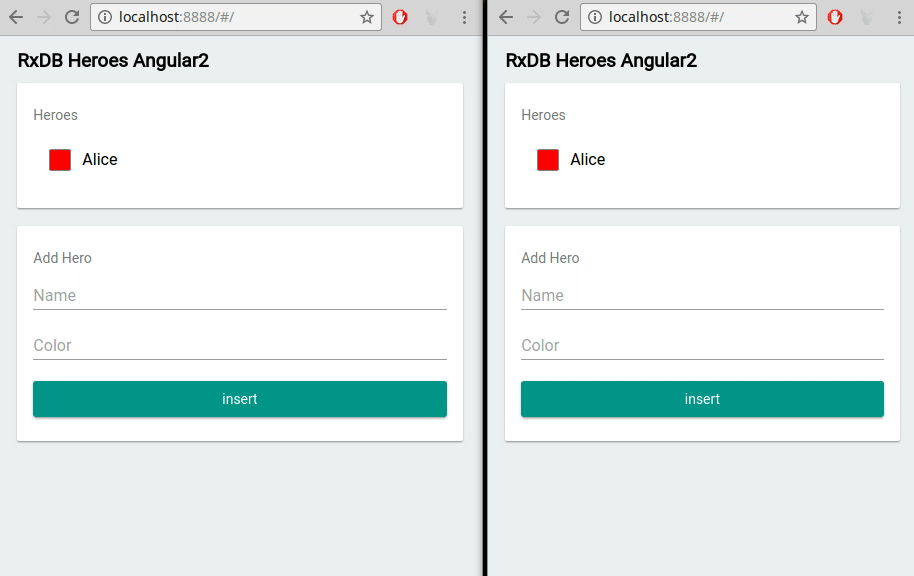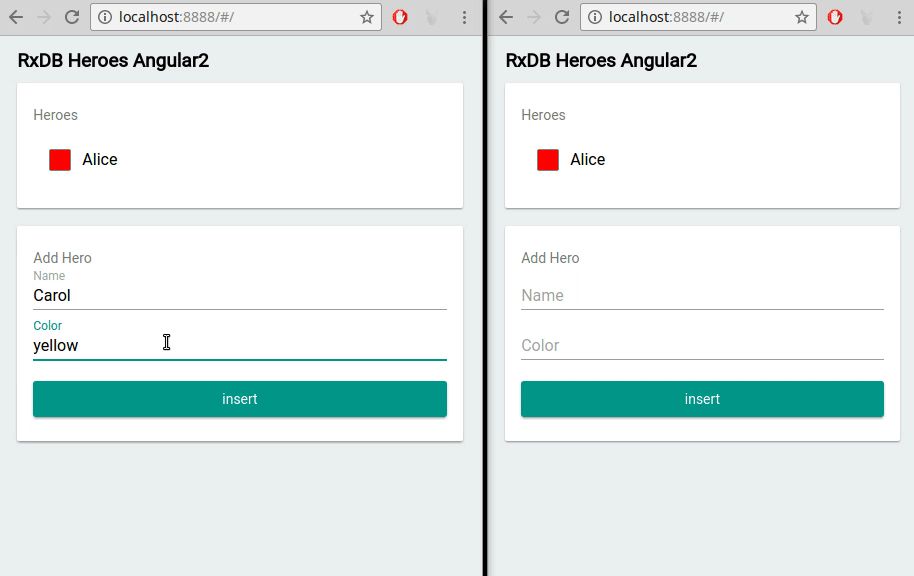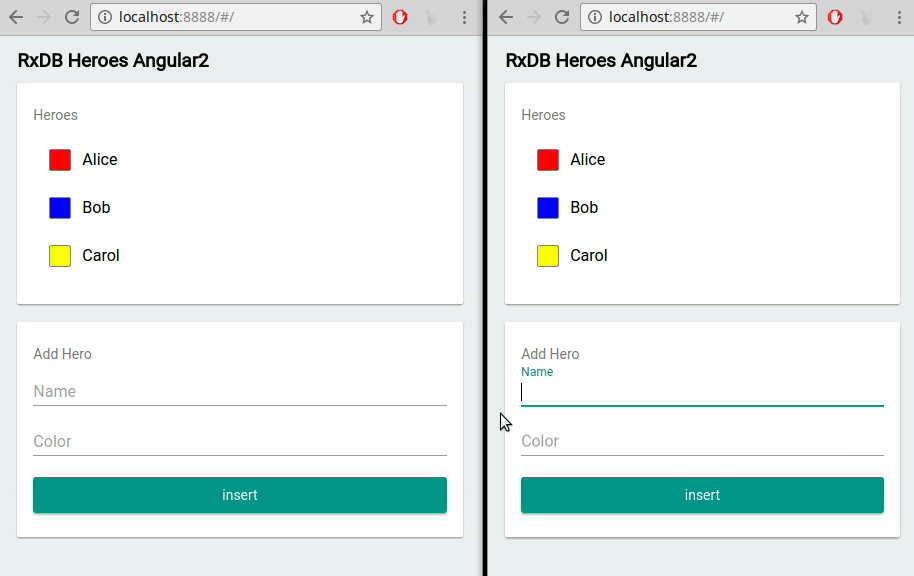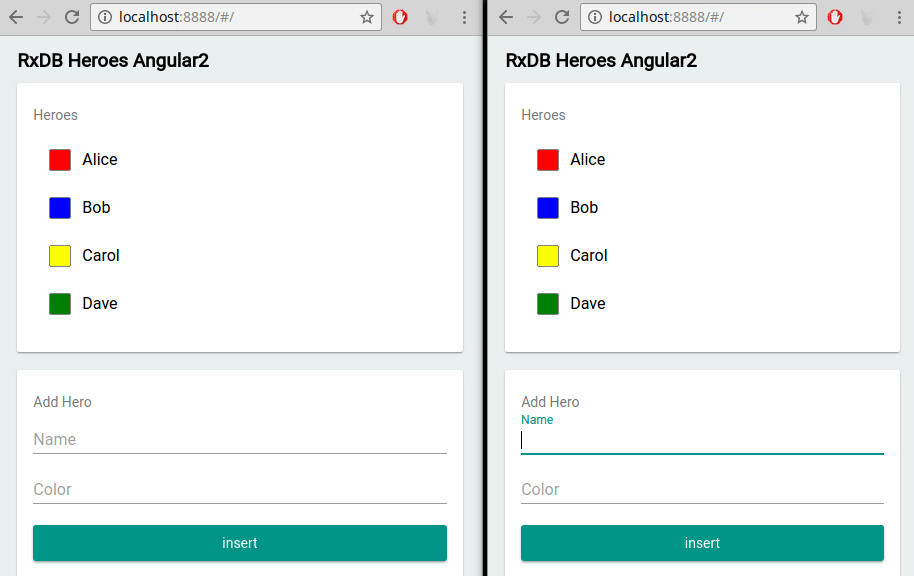
Multi-Tab Support
If your users open multiple tabs of your Vue application, RxDB ensures data is synchronized across all instances in real time. Changes made in one tab are immediately reflected in others, creating a unified user experience.
Best Practices for Using RxDB in Vue
Here are some recommendations to get the most out of RxDB in your Vue projects:
- Centralize Database Creation: Initialize and configure RxDB in a dedicated file or plugin, ensuring only one database instance is created.
- Leverage Vue's Composition API or a Global Store: Use watchers, refs, or a store like Pinia to neatly manage data subscriptions and updates, preventing scattered subscription logic.
- Async Subscriptions: Prefer using Vue's lifecycle hooks and the Composition API to manage subscriptions. Clean up subscriptions when components unmount or no longer need the data.
- Optimize Queries and Indexes: Only query the data you need, and define indexes to speed up lookups.
- Test Offline Scenarios: Make sure your offline logic works as expected by simulating network disconnections and reconnections.
- Plan Conflict Resolution: For multi-user apps, decide how to merge concurrent changes to prevent data inconsistencies.
Follow Up
To explore more about RxDB and leverage its capabilities for browser database development, check out the following resources:
- RxDB GitHub Repository: Visit the official GitHub repository of RxDB to access the source code, documentation, and community support.
- RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with RxDB by following the provided quickstart guide, which offers step-by-step instructions for setting up and using RxDB in your projects.
- RxDB Reactivity for Vue: Discover how RxDB observables can directly produce Vue refs, simplifying integration with your Vue components.
- RxDB Vue Example at GitHub: Explore an official Vue example to see RxDB in action within a Vue application.
- RxDB Examples: Browse even more official examples to learn best practices you can apply to your own projects.
 Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...
Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...