RxDB JavaScript Frontend Database: Efficient Data Storage in Frontend Applications
In modern web development, managing data on the front end has become increasingly important. Storing data in the frontend offers numerous advantages, such as offline accessibility, caching, faster application startup, and improved state management. Traditional SQL databases, although widely used on the server-side, are not always the best fit for frontend applications. This is where RxDB, a frontend JavaScript database, emerges as a powerful solution. In this article, we will explore why storing data in the frontend is beneficial, the limitations of SQL databases in the frontend, and how RxDB addresses these challenges to become an excellent choice for frontend data storage.
Why you might want to store data in the frontend
Offline accessibility
One compelling reason to store data in the frontend is to enable offline accessibility. By leveraging a frontend database, applications can cache essential data locally, allowing users to continue using the application even when an internet connection is unavailable. This feature is particularly useful for mobile applications or web apps with limited or intermittent connectivity.
Caching
Frontend databases also serve as efficient caching mechanisms. By storing frequently accessed data locally, applications can minimize network requests and reduce latency, resulting in faster and more responsive user experiences. Caching is particularly beneficial for applications that heavily rely on remote data or perform computationally intensive operations.
Decreased initial application start time
Storing data in the frontend decreases the initial application start time because the data is already present locally. By eliminating the need to fetch data from a server during startup, applications can quickly render the UI and provide users with an immediate interactive experience. This is especially advantageous for applications with large datasets or complex data retrieval processes.
Password encryption for local data
Security is a crucial aspect of data storage. With a front end database, developers can encrypt sensitive local data, such as user credentials or personal information, using encryption algorithms. This ensures that even if the device is compromised, the data remains securely stored and protected.
Local database for state management
Frontend databases provide an alternative to traditional state management libraries like Redux or NgRx. By utilizing a local database, developers can store and manage application state directly in the frontend, eliminating the need for additional libraries. This approach simplifies the codebase, reduces complexity, and provides a more straightforward data flow within the application.
Low-latency local queries
Frontend databases enable low-latency queries that run entirely on the client's device. Instead of relying on server round-trips for each query, the database executes queries locally, resulting in faster response times. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time updates or frequent data retrieval.

Building realtime applications with local data
Realtime applications often require immediate updates based on data changes. By storing data locally and utilizing a frontend database, developers can build realtime applications more easily. The database can observe data changes and automatically update the UI, providing a seamless and responsive user experience.
Easier integration with JavaScript frameworks
Frontend databases, including RxDB, are designed to integrate seamlessly with popular JavaScript frameworks such as Angular, React.js, Vue.js, and Svelte. These databases offer well-defined APIs and support that align with the specific requirements of these frameworks, enabling developers to leverage the full potential of the frontend database within their preferred development environment.
Simplified replication of database state
Replicating database state between the frontend and backend can be challenging, especially when dealing with complex REST routes. Frontend databases, however, provide simple mechanisms for replicating database state. They offer intuitive replication algorithms that facilitate data synchronization between the frontend and backend, reducing the complexity and potential pitfalls associated with complex REST-based replication.
Improved scalability
Frontend databases offer improved scalability compared to traditional SQL databases. By leveraging the computational capabilities of client devices, the burden on server resources is reduced. Queries and operations are performed locally, minimizing the need for server round-trips and enabling applications to scale more efficiently.
Why SQL databases are not a good fit for the front end of an application
While SQL databases excel in server-side scenarios, they pose limitations when used on the frontend. Here are some reasons why SQL databases are not well-suited for frontend applications:
Push/Pull based vs. reactive
SQL databases typically rely on a push/pull model, where the server pushes data to the client upon request. This approach is not inherently reactive, as it requires explicit requests for data updates. In contrast, frontend applications often require reactive data flows, where changes in data trigger automatic updates in the UI. Frontend databases, like RxDB, provide reactive capabilities that seamlessly integrate with the dynamic nature of frontend development.
Initialization time and performance
SQL databases designed for server-side usage tend to have larger build sizes and initialization times, making them less efficient for browser-based applications. Frontend databases, on the other hand, directly leverage browser APIs like IndexedDB, OPFS, and WebWorker, resulting in leaner builds and faster initialization times. Often the queries are such fast, that it is not even necessary to implement a loading spinner.

Build size considerations
Server-side SQL databases typically come with a significant build size, which can be impractical for browser applications where code size optimization is crucial. Frontend databases, on the other hand, are specifically designed to operate within the constraints of browser environments, ensuring efficient resource utilization and smaller build sizes.
For example the SQLite Webassembly file alone has a size of over 0.8 Megabyte with an additional 0.2 Megabyte in JavaScript code for connection.
Why RxDB is a good fit for the frontend
RxDB is a powerful frontend JavaScript database that addresses the limitations of SQL databases and provides an optimal solution for frontend data storage. Let's explore why RxDB is an excellent fit for frontend applications:
Made in JavaScript, optimized for JavaScript applications
RxDB is designed and optimized for JavaScript applications. Built using JavaScript itself, RxDB offers seamless integration with JavaScript frameworks and libraries, allowing developers to leverage their existing JavaScript knowledge and skills.
NoSQL (JSON) documents for UIs
RxDB adopts a NoSQL approach, using JSON documents as its primary data structure. This aligns well with the JavaScript ecosystem, as JavaScript natively works with JSON objects. By using NoSQL documents, RxDB provides a more natural and intuitive data model for UI-centric applications.
Better TypeScript support compared to SQL
TypeScript has become increasingly popular for building frontend applications. RxDB provides excellent TypeScript support, allowing developers to leverage static typing and benefit from enhanced code quality and tooling. This is particularly advantageous when compared to SQL databases, which often have limited TypeScript support.
Observable Queries for automatic UI updates
RxDB introduces the concept of observable queries, powered by RxJS. Observable queries automatically update the UI whenever there are changes in the underlying data. This reactive approach eliminates the need for manual UI updates and ensures that the frontend remains synchronized with the database state.
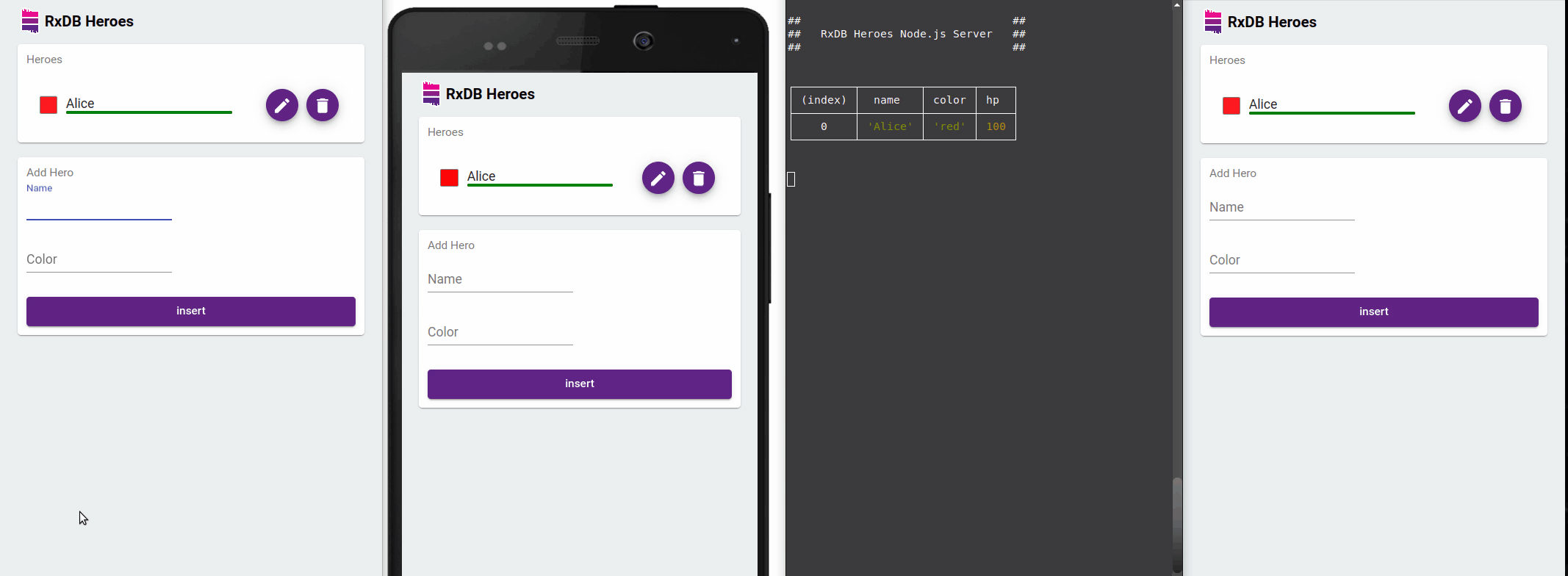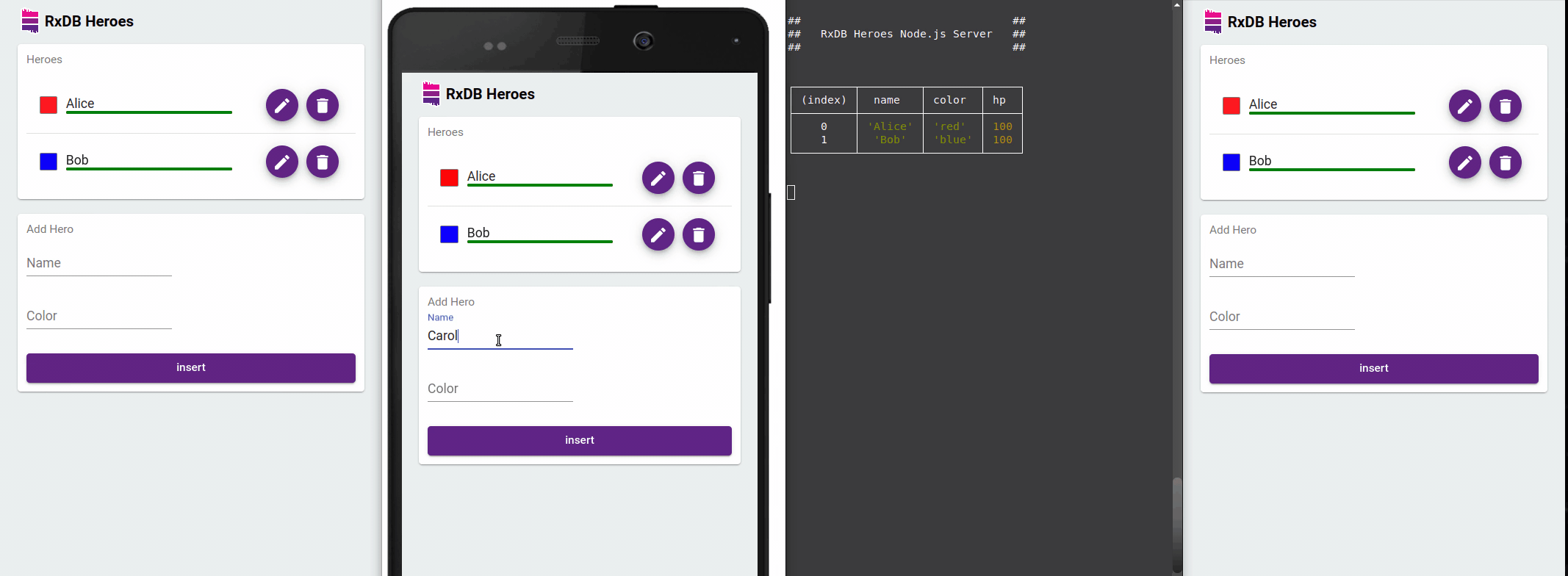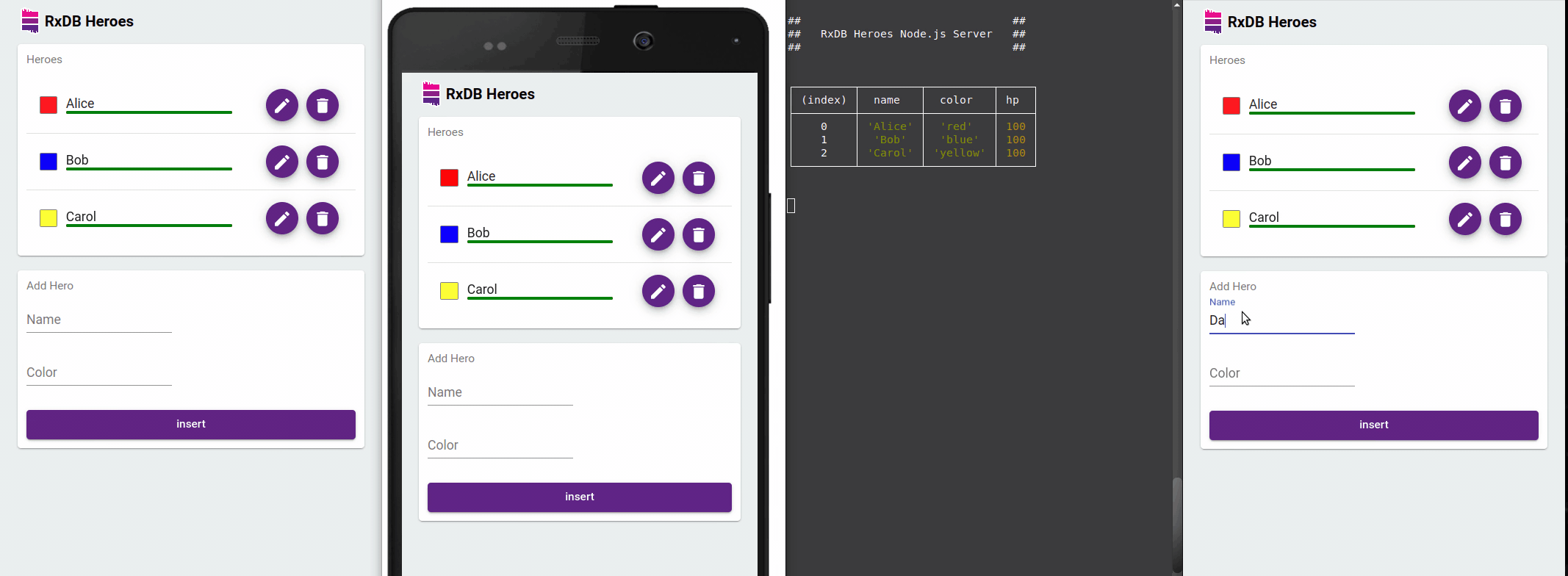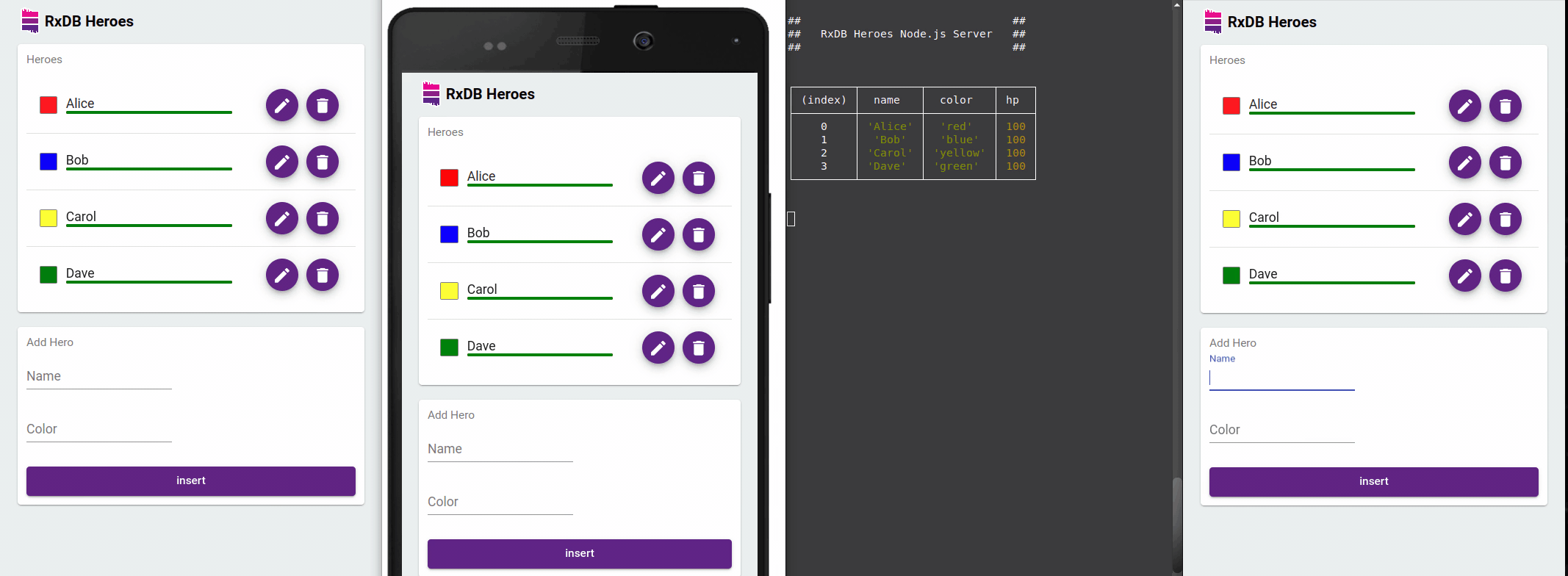
Optimized observed queries with the EventReduce Algorithm
RxDB optimizes observed queries with its EventReduce Algorithm. This algorithm intelligently reduces redundant events and ensures that UI updates are performed efficiently. By minimizing unnecessary re-renders, RxDB significantly improves performance and responsiveness in frontend applications.
const query = myCollection.find({
selector: {
age: {
$gt: 21
}
}
});
const querySub = query.$.subscribe(results => {
console.log('got results: ' + results.length);
});Observable document fields
RxDB supports observable document fields, enabling developers to track changes at a granular level within documents. By observing specific fields, developers can reactively update the UI when those fields change, ensuring a responsive and synchronized frontend interface.
myDocument.firstName$.subscribe(newName => console.log('name is: ' + newName));Storing Documents Compressed
RxDB provides the option to store documents in a compressed format, reducing storage requirements and improving overall database performance. Compressed storage offers benefits such as reduced disk space usage, faster data read/write operations, and improved network transfer speeds, making it an essential feature for efficient frontend data storage.
Built-in Multi-tab support
RxDB offers built-in multi-tab support, allowing data synchronization and state management across multiple browser tabs. This feature ensures consistent data access and synchronization, enabling users to work seamlessly across different tabs without conflicts or data inconsistencies.
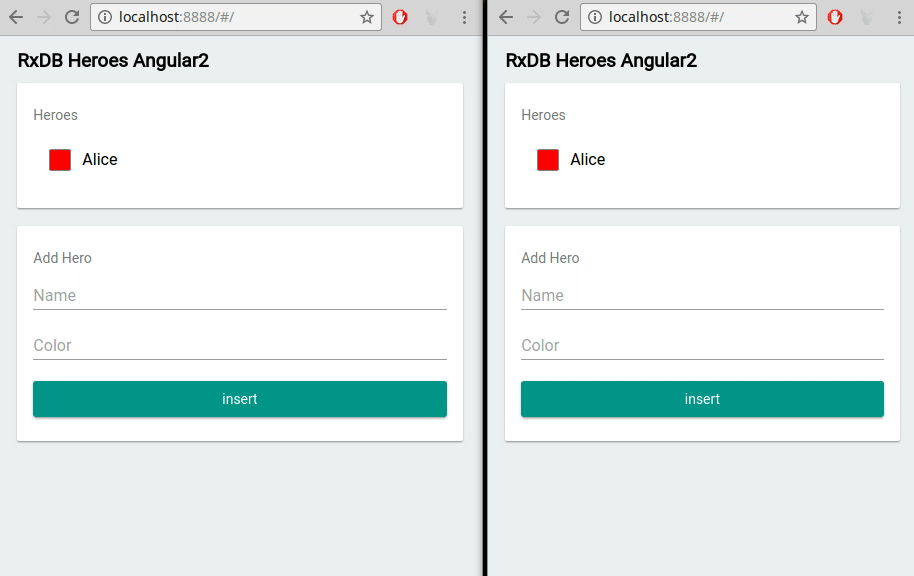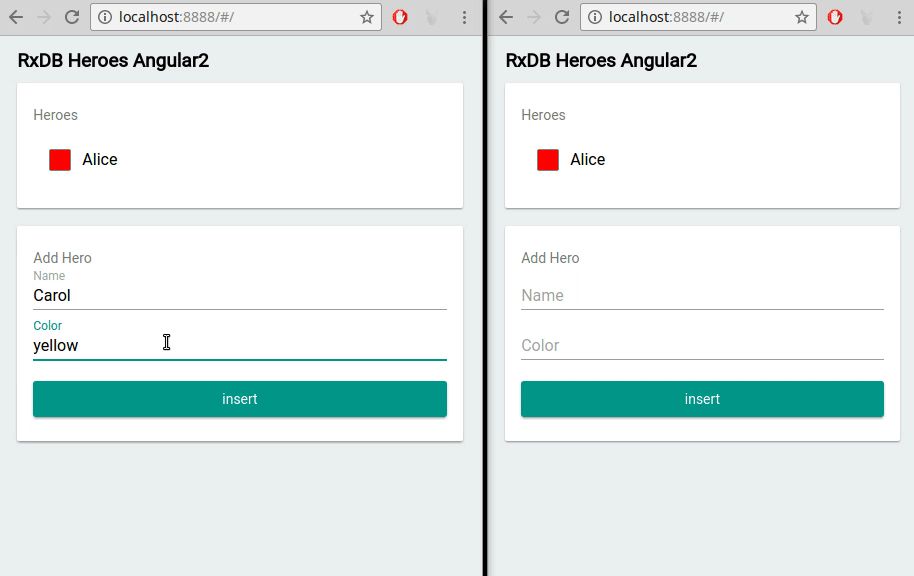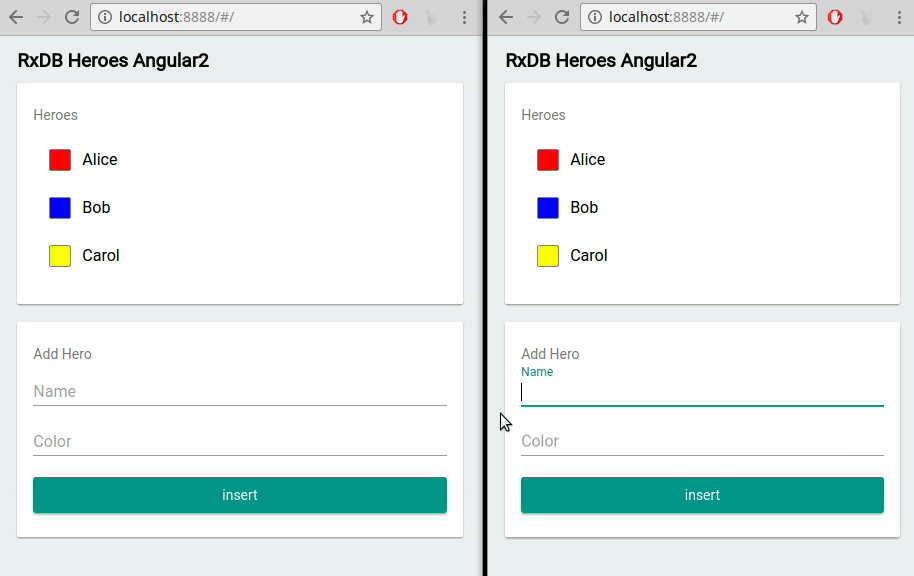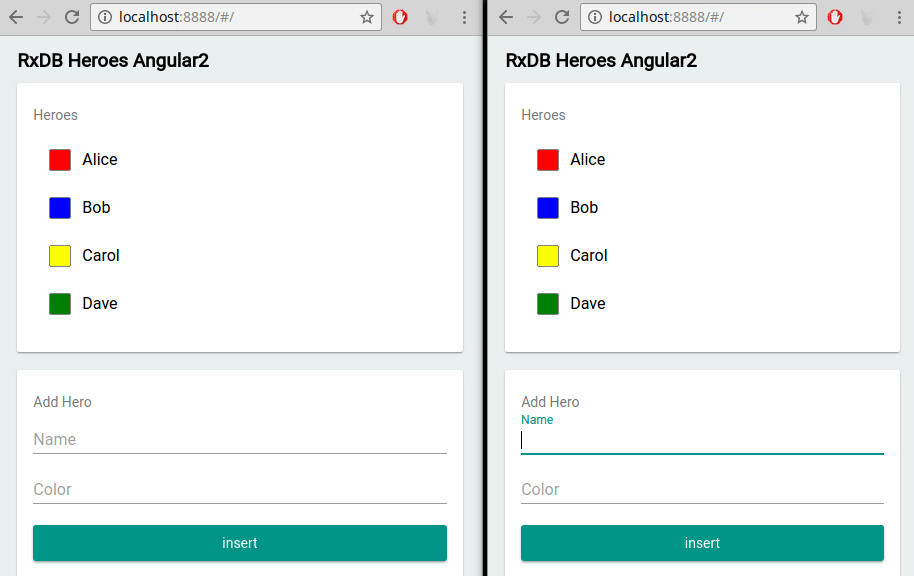
Replication Algorithm can be made compatible with any backend
RxDB's realtime replication algorithm is designed to be flexible and compatible with various backend systems. Whether you're using your own servers, Firebase, CouchDB, NATS, WebSocket, or any other backend, RxDB can be seamlessly integrated and synchronized with the backend system of your choice.
Flexible storage layer for code reuse
RxDB provides a flexible storage layer that enables code reuse across different platforms. Whether you're building applications with Electron.js, React Native, hybrid apps using Capacitor.js, or traditional web browsers, RxDB allows you to reuse the same codebase and leverage the power of a frontend database across different environments.
Handling schema changes in distributed environments
In distributed environments where data is stored on multiple client devices, handling schema changes can be challenging. RxDB tackles this challenge by providing robust mechanisms for handling schema changes. It ensures that schema updates propagate smoothly across devices, maintaining data integrity and enabling seamless schema evolution.
Follow Up
To further explore RxDB and get started with using it in your frontend applications, consider the following resources:
- RxDB Quickstart: A step-by-step guide to quickly set up RxDB in your project and start leveraging its features.
- RxDB GitHub Repository: The official repository for RxDB, where you can find the code, examples, and community support.
By adopting RxDB as your frontend database, you can unlock the full potential of frontend data storage and empower your applications with offline accessibility, caching, improved performance, and seamless data synchronization. RxDB's JavaScript-centric approach and powerful features make it an ideal choice for frontend developers seeking efficient and scalable data storage solutions.
 Ask a question on the forums about RxDB - The Ultimate JS...
Ask a question on the forums about RxDB - The Ultimate JS...