RxDB as a Database in an Angular Application
In modern web development, Angular has emerged as a popular framework for building robust and scalable applications. As Angular applications often require persistent storage and efficient data handling, choosing the right database solution is crucial. One such solution is RxDB, a reactive JavaScript database for the browser, node.js, and mobile devices. In this article, we will explore the integration of RxDB into an Angular application and examine its various features and techniques.
Angular Web Applications
Angular is a powerful JavaScript framework developed and maintained by Google. It enables developers to build single-page applications (SPAs) with a modular and component-based approach. Angular provides a comprehensive set of tools and features for creating dynamic and responsive web applications.
Importance of Databases in Angular Applications
Databases play a vital role in Angular applications by providing a structured and efficient way to store, retrieve, and manage data. Whether it's handling user authentication, caching data, or persisting application state, a robust database solution is essential for ensuring optimal performance and user experience.
Introducing RxDB as a Database Solution
RxDB stands for Reactive Database and is built on the principles of reactive programming. It combines the best features of NoSQL databases with the power of reactive programming to provide a scalable and efficient database solution. RxDB offers seamless integration with Angular applications and brings several unique features that make it an attractive choice for developers.
Getting Started with RxDB
To begin our journey with RxDB, let's understand its key concepts and features.
What is RxDB?
RxDB is a client-side database that follows the principles of reactive programming. It is built on top of IndexedDB, the native browser database, and leverages the RxJS library for reactive data handling. RxDB provides a simple and intuitive API for managing data and offers features like data replication, multi-tab support, and efficient query handling.
Reactive Data Handling
At the core of RxDB is the concept of reactive data handling. RxDB leverages observables and reactive streams to enable real-time updates and data synchronization. With RxDB, you can easily subscribe to data changes and react to them in a reactive and efficient manner.
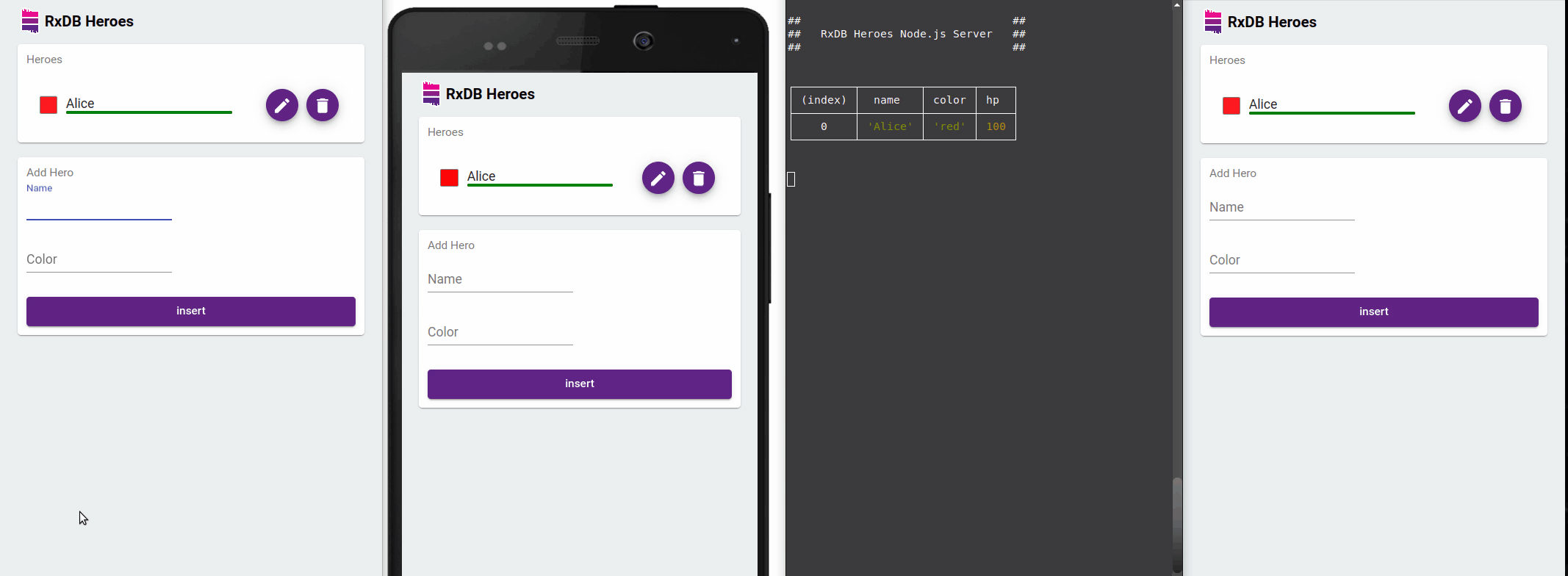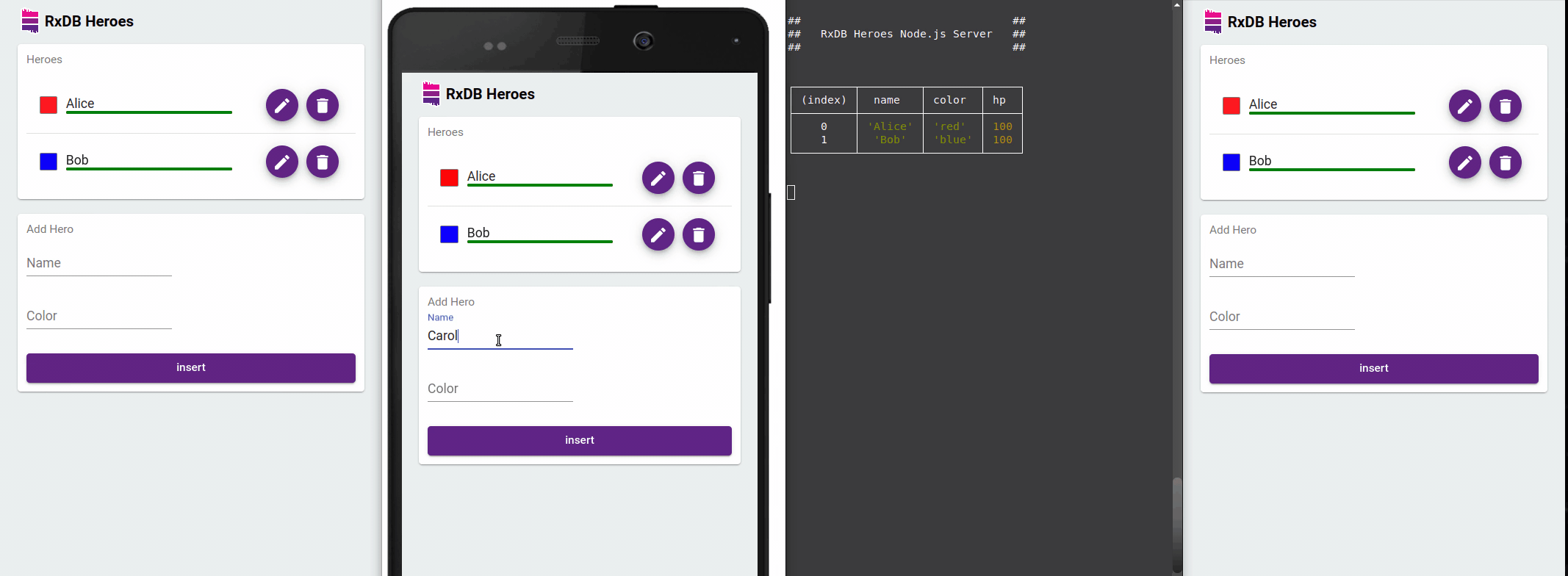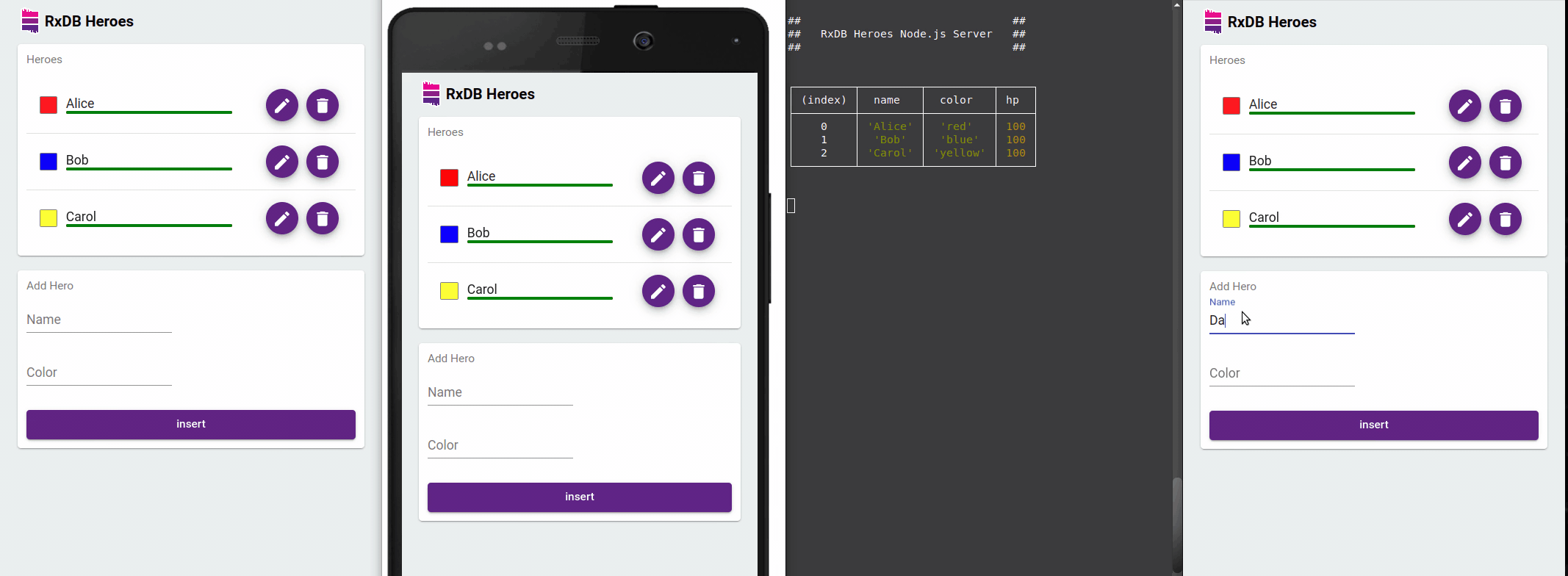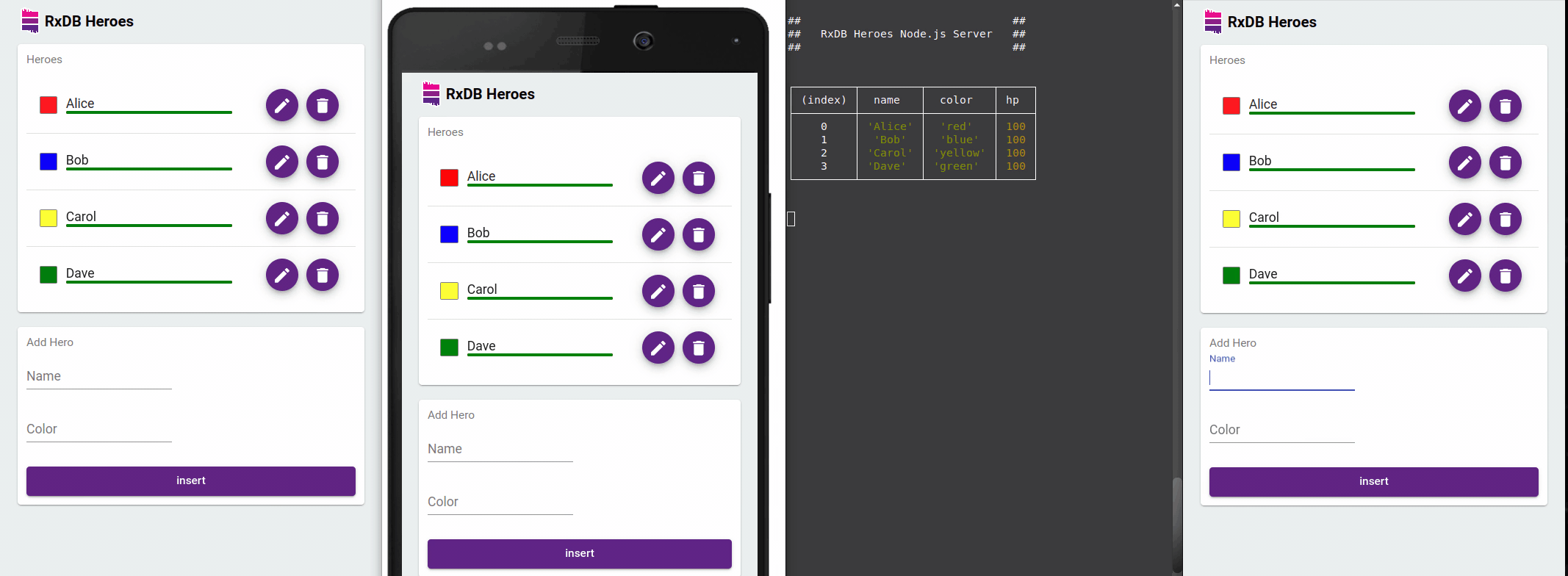
Offline-First Approach
One of the standout features of RxDB is its offline-first approach. It allows you to build applications that can work seamlessly in offline scenarios. RxDB stores data locally and automatically synchronizes changes with the server when the network becomes available. This capability is particularly useful for applications that need to function in low-connectivity or unreliable network environments.
Data Replication
RxDB provides built-in support for data replication between clients and servers. This means you can synchronize data across multiple devices or instances of your application effortlessly. RxDB handles conflict resolution and ensures that data remains consistent across all connected clients.
Observable Queries
RxDB offers a powerful querying mechanism with support for observable queries. This allows you to create dynamic queries that automatically update when the underlying data changes. By leveraging RxDB's observable queries, you can build reactive UI components that respond to data changes in real-time.
Multi-Tab Support
RxDB provides out-of-the-box support for multi-tab scenarios. This means that if your Angular application is running in multiple browser tabs, RxDB automatically keeps the data in sync across all tabs. It ensures that changes made in one tab are immediately reflected in others, providing a seamless user experience.
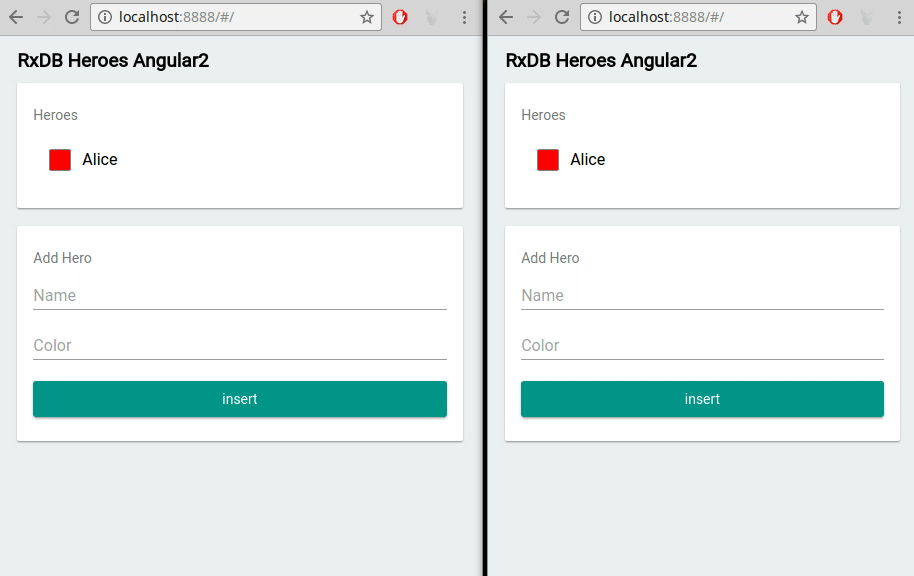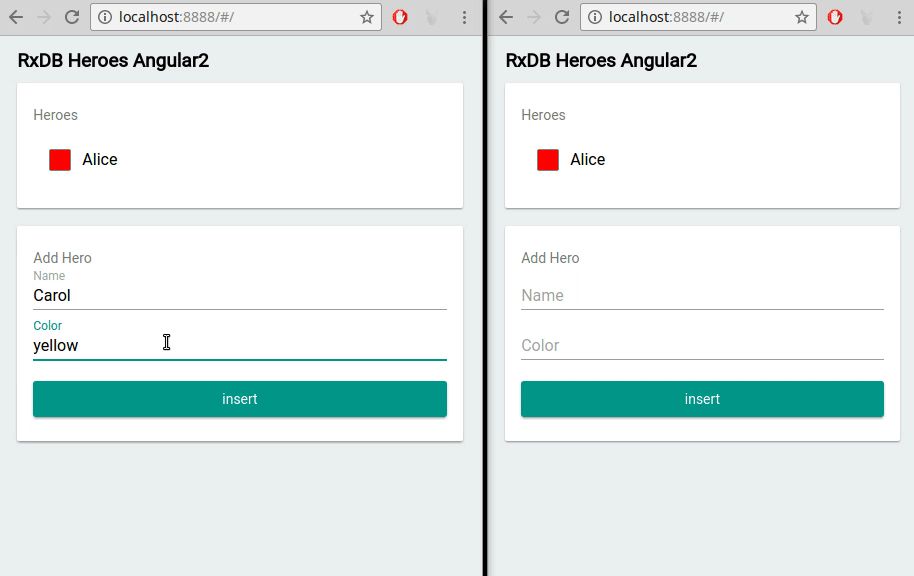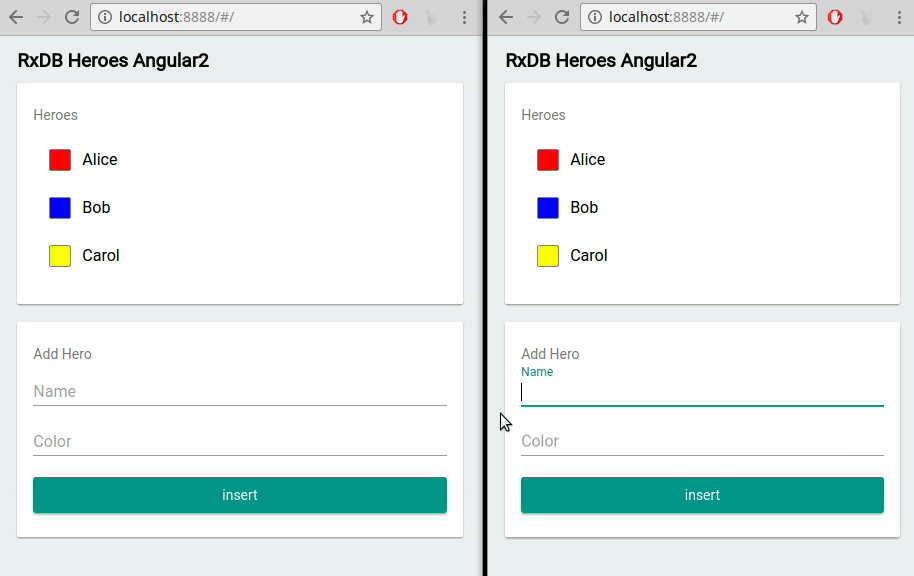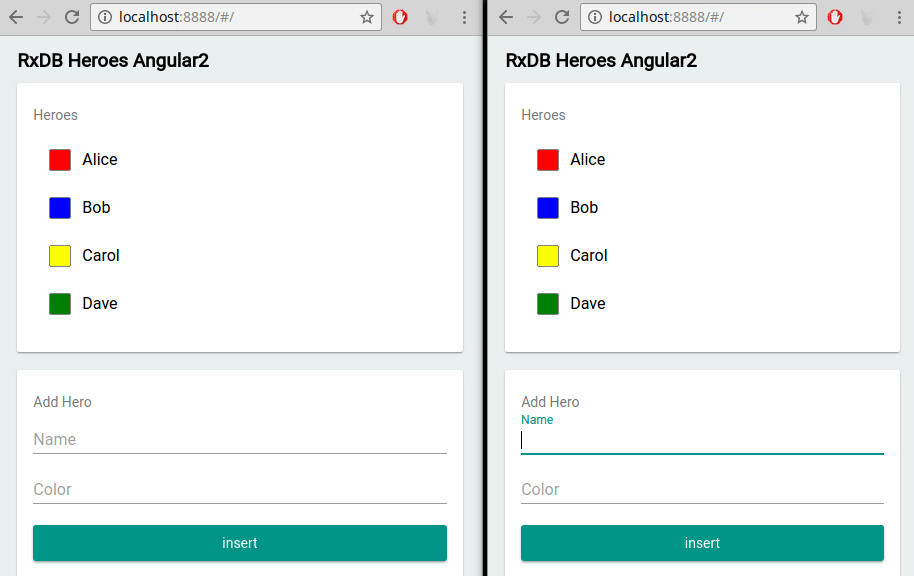
RxDB vs. Other Angular Database Options
While there are other database options available for Angular applications, RxDB stands out with its reactive programming model, offline-first approach, and built-in synchronization capabilities. Unlike traditional SQL databases, RxDB's NoSQL-like structure and observables-based API make it well-suited for real-time applications and complex data scenarios.
Using RxDB in an Angular Application
Now that we have a good understanding of RxDB and its features, let's explore how to integrate it into an Angular application.
Installing RxDB in an Angular App
To use RxDB in an Angular application, we first need to install the necessary dependencies. You can install RxDB using npm or yarn by running the following command:
npm install rxdb --saveOnce installed, you can import RxDB into your Angular application and start using its API to create and manage databases.
Patch Change Detection with zone.js
Angular uses change detection to detect and update UI elements when data changes. However, RxDB's data handling is based on observables, which can sometimes bypass Angular's change detection mechanism. To ensure that changes made in RxDB are detected by Angular, we need to patch the change detection mechanism using zone.js. Zone.js is a library that intercepts and tracks asynchronous operations, including observables. By patching zone.js, we can make sure that Angular is aware of changes happening in RxDB.
RxDB creates rxjs observables outside of angulars zone So you have to import the rxjs patch to ensure the angular change detection works correctly. link
//> app.component.ts
import 'zone.js/plugins/zone-patch-rxjs';Use the Angular async pipe to observe an RxDB Query
Angular provides the async pipe, which is a convenient way to subscribe to observables and handle the subscription lifecycle automatically. When working with RxDB, you can use the async pipe to observe an RxDB query and bind the results directly to your Angular template. This ensures that the UI stays in sync with the data changes emitted by the RxDB query.
constructor(
private dbService: DatabaseService,
private dialog: MatDialog
) {
this.heroes$ = this.dbService
.db.hero // collection
.find({ // query
selector: {},
sort: [{ name: 'asc' }]
})
.$;
}<ul *ngFor="let hero of heroes$ | async as heroes;">
<li>{{hero.name}}</li>
</ul>Different RxStorage layers for RxDB
RxDB supports multiple storage layers for persisting data. Some of the available storage options include:
- LocalStorage RxStorage: Uses the LocalStorage API without any third party plugins.
- IndexedDB RxStorage: RxDB directly supports IndexedDB as a storage layer. IndexedDB is a low-level browser database that offers good performance and reliability.
- OPFS RxStorage: The OPFS RxStorage for RxDB is built on top of the File System Access API which is available in all modern browsers. It provides an API to access a sandboxed private file system to persistently store and retrieve data. Compared to other persistent storage options in the browser (like IndexedDB), the OPFS API has a way better performance.
- Memory RxStorage: In addition to persistent storage options, RxDB also provides a memory-based storage layer. This is useful for testing or scenarios where you don't need long-term data persistence. You can choose the storage layer that best suits your application's requirements and configure RxDB accordingly.
Synchronizing Data with RxDB between Clients and Servers
Data replication between an Angular application and a server is a common requirement. RxDB simplifies this process and provides built-in support for data synchronization. Let's explore how to replicate data between an Angular application and a server using RxDB.
Offline-First Approach
One of the key strengths of RxDB is its offline-first approach. It allows Angular applications to function seamlessly even in offline scenarios. RxDB stores data locally and automatically synchronizes changes with the server when the network becomes available. This capability is particularly useful for applications that need to operate in low-connectivity or unreliable network environments.
Conflict Resolution
In a distributed system, conflicts can arise when multiple clients modify the same data simultaneously. RxDB offers conflict resolution mechanisms to handle such scenarios. You can define conflict resolution strategies based on your application's requirements. RxDB provides hooks and events to detect conflicts and resolve them in a consistent manner.
Bidirectional Synchronization
RxDB supports bidirectional data synchronization, allowing updates from both the client and server to be replicated seamlessly. This ensures that data remains consistent across all connected clients and the server. RxDB handles conflicts and resolves them based on the defined conflict resolution strategies.
Real-Time Updates
RxDB provides real-time updates by leveraging reactive programming principles. Changes made to the data are automatically propagated to all connected clients in real-time. Angular applications can subscribe to these updates and update the user interface accordingly. This real-time capability enables collaborative features and enhances the overall user experience.
Advanced RxDB Features and Techniques
RxDB offers several advanced features and techniques that can further enhance your Angular application.
Indexing and Performance Optimization
To improve query performance, RxDB allows you to define indexes on specific fields of your documents. Indexing enables faster data retrieval and query execution, especially when working with large datasets. By strategically creating indexes, you can optimize the performance of your Angular application.
Encryption of Local Data
RxDB provides built-in support for encrypting local data using the Web Crypto API. With encryption, you can protect sensitive data stored in the client-side database. RxDB transparently encrypts the data, ensuring that it remains secure even if the underlying storage is compromised.
Change Streams and Event Handling
RxDB exposes change streams, which allow you to listen for data changes at a database or collection level. By subscribing to change streams, you can react to data modifications and perform specific actions, such as updating the UI or triggering notifications. Change streams enable real-time event handling in your Angular application.
JSON Key Compression
To reduce the storage footprint and improve performance, RxDB supports JSON key compression. With key compression, RxDB replaces long keys with shorter aliases, reducing the overall storage size. This optimization is particularly useful when working with large datasets or frequently updating data.
Best Practices for Using RxDB in Angular Applications
To make the most of RxDB in your Angular application, consider the following best practices:
Use Async Pipe for Subscriptions so you do not have to unsubscribe
Angular's async pipe is a powerful tool for handling observables in templates. By using the async pipe, you can avoid the need to manually subscribe and unsubscribe from RxDB observables. Angular takes care of the subscription lifecycle, ensuring that resources are released when they are no longer needed. Instead of manually subscribing to Observables, you should always prefer the async pipe.
// WRONG:
let amount;
this.dbService
.db.hero
.find({
selector: {},
sort: [{ name: 'asc' }]
})
.$.subscribe(docs => {
amount = 0;
docs.forEach(d => amount = d.points);
});
// RIGHT:
this.amount$ = this.dbService
.db.hero
.find({
selector: {},
sort: [{ name: 'asc' }]
})
.$.pipe(
map(docs => {
let amount = 0;
docs.forEach(d => amount = d.points);
return amount;
})
);Use custom reactivity to have signals instead of rxjs observables
RxDB supports adding custom reactivity factories that allow you to get angular signals out of the database instead of rxjs observables. read more.
Use Angular Services for Database creation
To ensure proper separation of concerns and maintain a clean codebase, it is recommended to create an Angular service responsible for managing the RxDB database instance. This service can handle database creation, initialization, and provide methods for interacting with the database throughout your application.
Efficient Data Handling
RxDB provides various mechanisms for efficient data handling, such as batching updates, debouncing, and throttling. Leveraging these techniques can help optimize performance and reduce unnecessary UI updates. Consider the specific data handling requirements of your application and choose the appropriate strategies provided by RxDB.
Data Synchronization Strategies
When working with data synchronization between clients and servers, it's important to consider strategies for conflict resolution and handling network failures. RxDB provides plugins and hooks that allow you to customize the replication behavior and implement specific synchronization strategies tailored to your application's needs.
Conclusion
RxDB is a powerful database solution for Angular applications, offering reactive data handling, offline-first capabilities, and seamless data synchronization. By integrating RxDB into your Angular application, you can build responsive and scalable web applications that provide a rich user experience. Whether you're building real-time collaborative apps, progressive web applications, or offline-capable applications, RxDB's features and techniques make it a valuable addition to your Angular development toolkit.
Follow Up
To explore more about RxDB and leverage its capabilities for browser database development, check out the following resources:
- RxDB GitHub Repository: Visit the official GitHub repository of RxDB to access the source code, documentation, and community support.
- RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with RxDB by following the provided quickstart guide, which provides step-by-step instructions for setting up and using RxDB in your projects.
- RxDB Angular Example at GitHub

 Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...
Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...