Build Smarter Offline-First Angular Apps: How RxDB Beats IndexedDB Alone
In modern web applications, offline capabilities and fast interactions are crucial. IndexedDB, the browser's built-in database, allows you to store data locally, making your Angular application more robust and responsive. However, IndexedDB can be cumbersome to work with directly. That's where RxDB (Reactive Database) shines. In this article, we'll walk you through how to utilize IndexedDB in your Angular project using RxDB as a convenient abstraction layer.
What Is IndexedDB?
IndexedDB is a low-level JavaScript API for client-side storage of large amounts of structured data. It allows you to create key-value or object store-based data storage right in the user's browser. IndexedDB supports transactions and indexing but lacks a robust query API and can be complex to use due to its callback-based nature.
Why Use IndexedDB in Angular
-
Offline-First/Local-First: If your app needs to function with limited or no internet connectivity, IndexedDB provides a reliable local storage layer. Users can continue using the application offline, and data can sync when the connection is restored.
-
Performance: Local data access comes with near-zero latency, removing the need for constant server requests and eliminating most loading spinners.
-
Easier to Implement: By replicating all necessary data to the client once, you avoid implementing numerous backend endpoints for each user interaction.
-
Scalability: Local data queries remove processing load from your servers and reduce bandwidth usage by handling queries on the client side.
Why Using Plain IndexedDB is a Problem
Despite the advantages, directly working with IndexedDB has several drawbacks:
-
Callback-Based: IndexedDB was originally designed around a callback-based API, which can be unwieldy compared to modern Promise or RxJS-based flows.
-
Difficult to Implement: IndexedDB is often described as a "low-level" API. It's more suitable for library authors rather than application developers who simply need a robust local store.
-
Rudimentary Query API: Complex or dynamic queries are cumbersome with IndexedDB's basic get/put approach and limited indexes.
-
TypeScript Support: Maintaining strong TypeScript types for all document structures is not straightforward with IndexedDB's untyped object stores.
-
No Observable API: IndexedDB cannot directly emit live data changes. With RxDB, you can subscribe to changes on a collection or even a single document field.
-
Cross-Tab Synchronization: Handling concurrent data changes across multiple browser tabs is difficult in IndexedDB. RxDB has built-in multi-tab support that keeps all tabs in sync.
-
Advanced Features Missing: IndexedDB lacks built-in support for encryption, compression, or other advanced data management features.
-
Browser-Only: IndexedDB works in the browser but not in environments like React Native or Electron. RxDB offers storage adapters to seamlessly reuse the same code on different platforms.
Set Up RxDB in Angular
Installing RxDB
You can install RxDB into your Angular application via npm:
npm install rxdb --savePatch Change Detection with zone.js
RxDB creates RxJS observables outside of Angular's zone, meaning Angular won't automatically trigger change detection when new data arrives. You must patch RxJS with zone.js:
//> app.component.ts
/**
* IMPORTANT: RxDB creates rxjs observables outside of Angular's zone
* So you have to import the rxjs patch to ensure change detection works correctly.
* @link https://www.bennadel.com/blog/3448-binding-rxjs-observable-sources-outside-of-the-ngzone-in-angular-6-0-2.htm
*/
import 'zone.js/plugins/zone-patch-rxjs';Create a Database and Collections
RxDB supports multiple storage options. The free and simple approach is using the localstorage-based storage. For higher performance, there's a premium plain IndexedDB storage.
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb/plugins/core';
// Define your schema
const heroSchema = {
title: 'hero schema',
version: 0,
description: 'Describes a hero in your app',
primaryKey: 'id',
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: {
type: 'string',
maxLength: 100
},
name: {
type: 'string'
},
power: {
type: 'string'
}
},
required: ['id', 'name']
};import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
export async function initDB() {
// Create a database
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'heroesdb', // the name of the database
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage()
});
// Add collections
await db.addCollections({
heroes: {
schema: heroSchema
}
});
return db;
}It's recommended to encapsulate database creation logic in an Angular service, such as in a DatabaseService. A full example is available in RxDB's Angular example.
CRUD Operations
Once your database is initialized, you can perform all CRUD operations:
// insert
await db.heroes.insert({ name: 'Iron Man', power: 'Genius-level intellect' });
// bulk insert
await db.heroes.bulkInsert([
{ name: 'Thor', power: 'God of Thunder' },
{ name: 'Hulk', power: 'Superhuman Strength' }
]);
// find and findOne
const heroes = await db.heroes.find().exec();
const ironMan = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Iron Man' } }).exec();
// update
const doc = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Hulk' } }).exec();
await doc.update({ $set: { power: 'Unlimited Strength' } });
// delete
const doc = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Thor' } }).exec();
await doc.remove();Reactive Queries and Live Updates
A key benefit of RxDB is reactivity. You can subscribe to changes and have your UI automatically reflect updates in real time even across browser tabs.
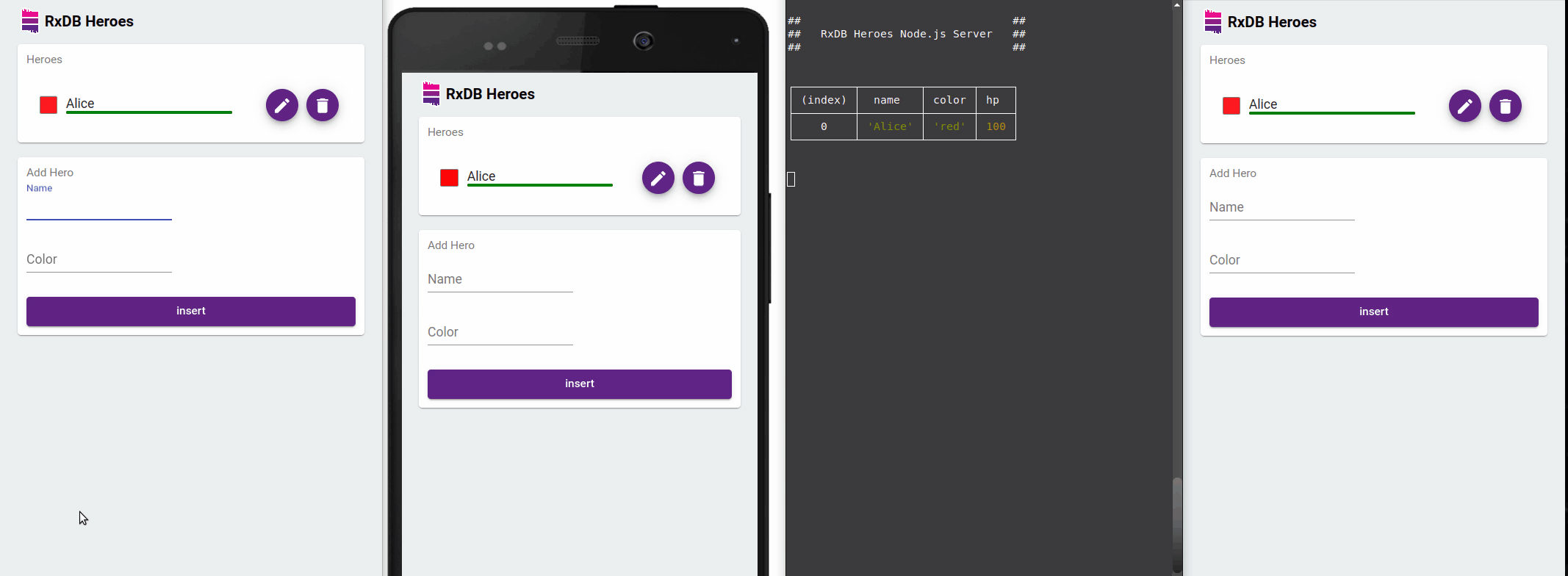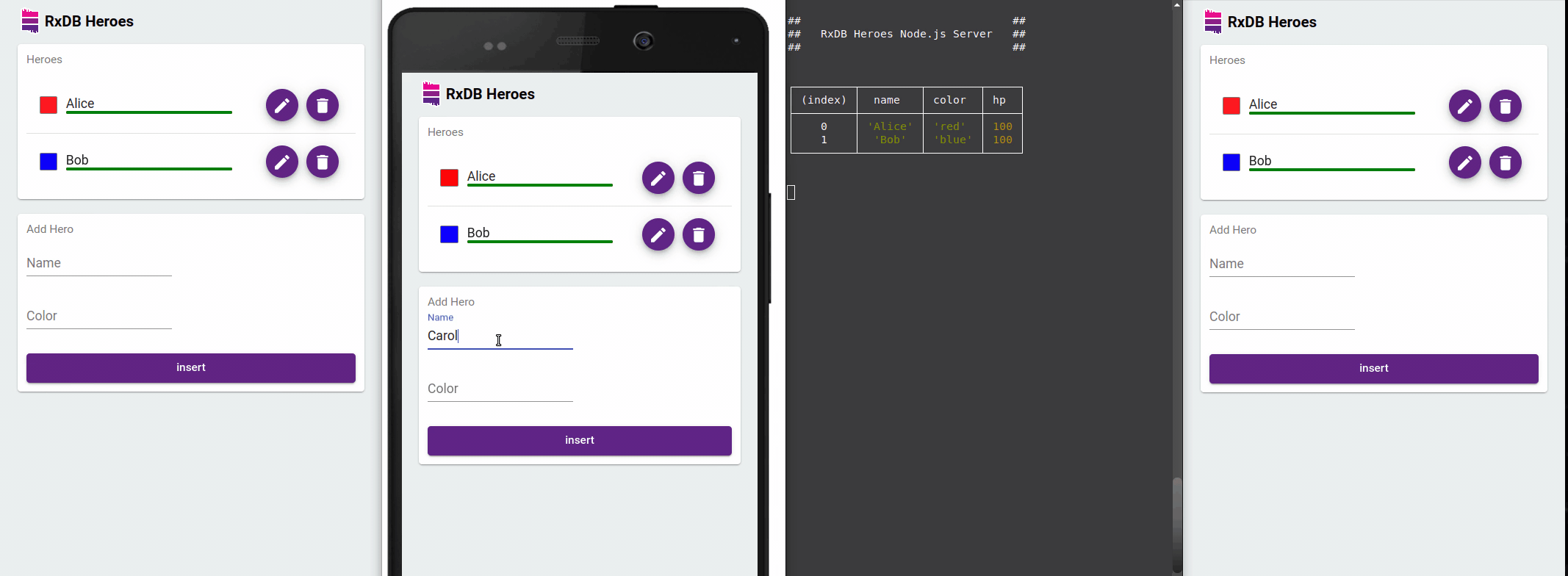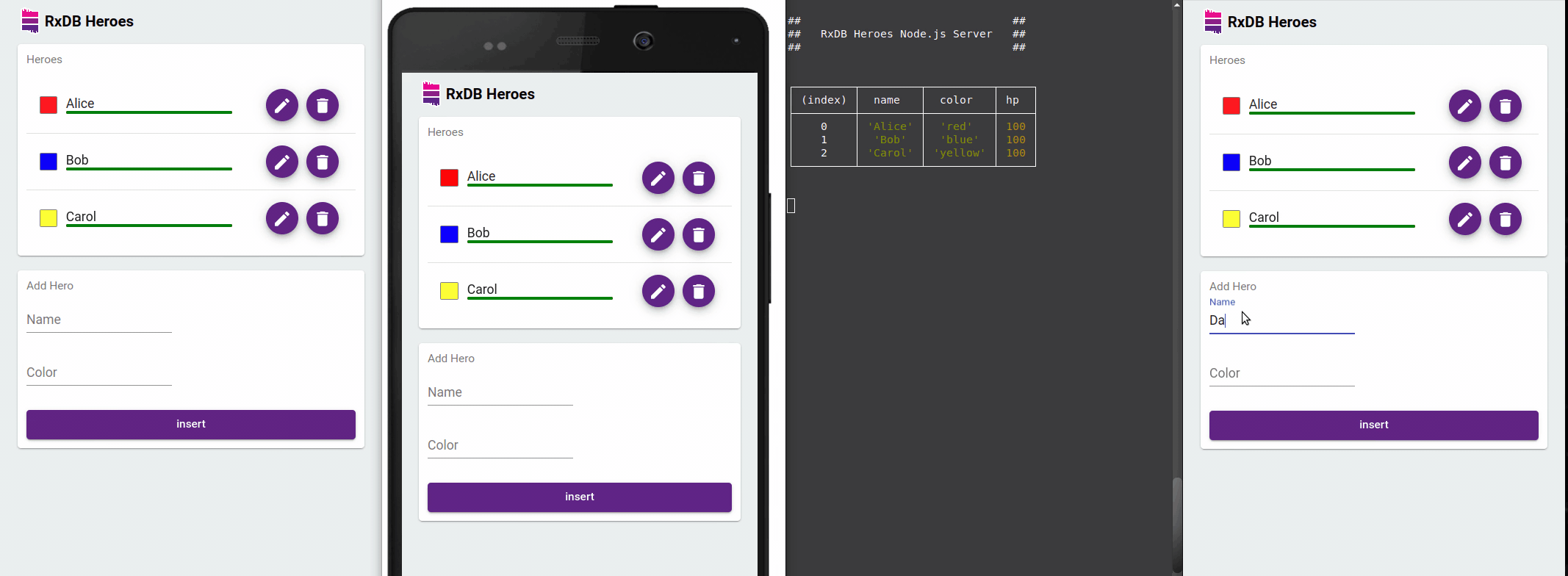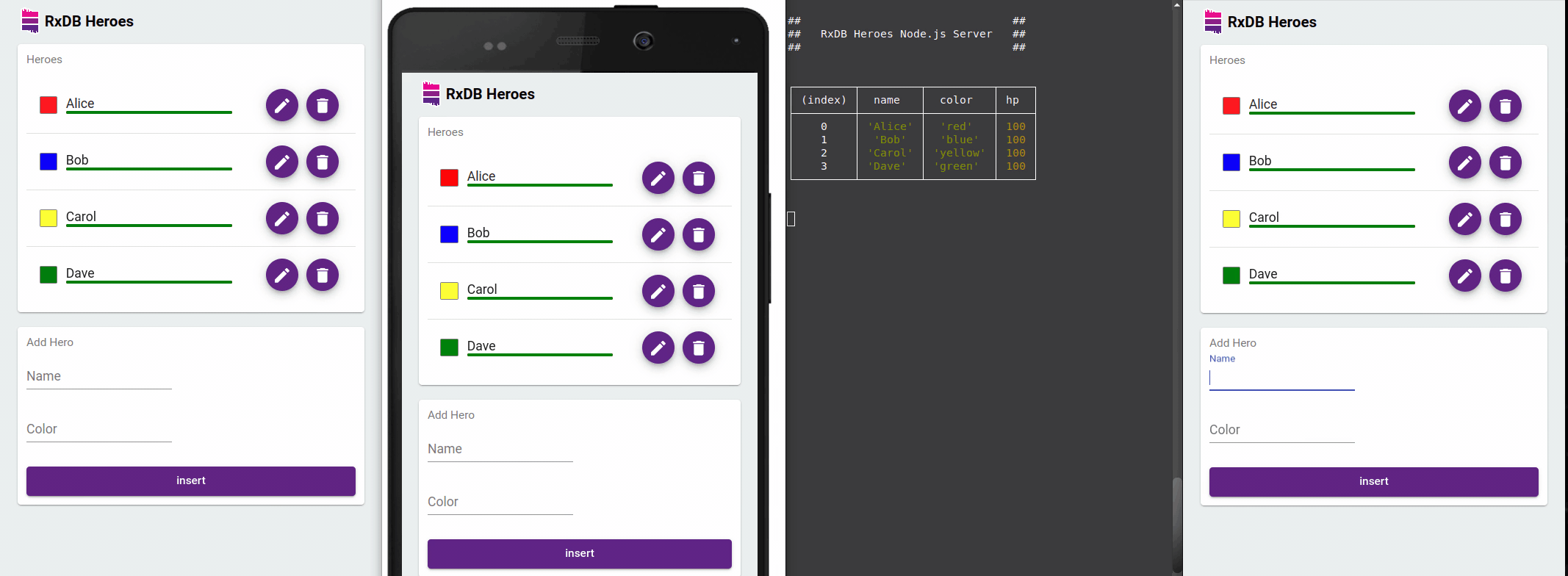
With RxJS Observables and Async Pipes
In Angular, you can display this data with the AsyncPipe:
constructor(private dbService: DatabaseService) {
this.heroes$ = this.dbService.db.heroes.find({
selector: {},
sort: [{ name: 'asc' }]
}).$;
}<ul>
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroes$ | async">
{{ hero.name }}
</li>
</ul>With Angular Signals
Angular Signals are a newer approach for reactivity. RxDB supports them via a custom reactivity factory. You can convert RxJS Observables to Signals using Angular's toSignal:
import { RxReactivityFactory } from 'rxdb/plugins/core';
import { Signal, untracked, Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { toSignal } from '@angular/core/rxjs-interop';
export function createReactivityFactory(injector: Injector): RxReactivityFactory<Signal<any>> {
return {
fromObservable(observable$, initialValue) {
return untracked(() =>
toSignal(observable$, {
initialValue,
injector,
rejectErrors: true
})
);
}
};
}Pass this factory when creating your RxDatabase:
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb/plugins/core';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
import { inject, Injector } from '@angular/core';
const database = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'mydb',
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage(),
reactivity: createReactivityFactory(inject(Injector))
});Use the double-dollar sign ($$) to get a Signal instead of an Observable:
const heroesSignal = database.heroes.find().$$;<ul>
<li *ngFor="let hero of heroesSignal()">
{{ hero.name }}
</li>
</ul>Angular IndexedDB Example with RxDB
A comprehensive example of RxDB in an Angular application is available in the RxDB GitHub repository. It demonstrates database creation, queries, and Angular integration using best practices.
Advanced RxDB Features
Beyond simple CRUD and local data storage, RxDB supports:
-
Replication: Sync your local data with a remote database. Learn more at RxDB Replication.
-
Data Migration on Schema Changes: RxDB supports automatic or manual schema migrations to manage backward-compatibility and evolve your data structure. See RxDB Migration.
-
Encryption: Easily encrypt sensitive data at rest. See RxDB Encryption.
-
Compression: Reduce storage and bandwidth usage using key compression. Learn more at RxDB Key Compression.
Limitations of IndexedDB
While IndexedDB works well for many use cases, it does have a few constraints:
-
Potentially Slow: While adequate for most use cases, IndexedDB performance can degrade for very large datasets. More details at RxDB Slow IndexedDB.
-
Storage Limits: Browsers may cap the amount of data you can store in IndexedDB. For more info, see Local Storage Limits of IndexedDB.
Alternatives to IndexedDB
Depending on your needs, you might explore:
-
Origin Private File System (OPFS): A newer browser storage mechanism that can offer better performance. RxDB supports OPFS storage.
-
SQLite: When building a mobile or hybrid app (e.g., with Capacitor or Ionic), you can use SQLite locally. See RxDB with SQLite.
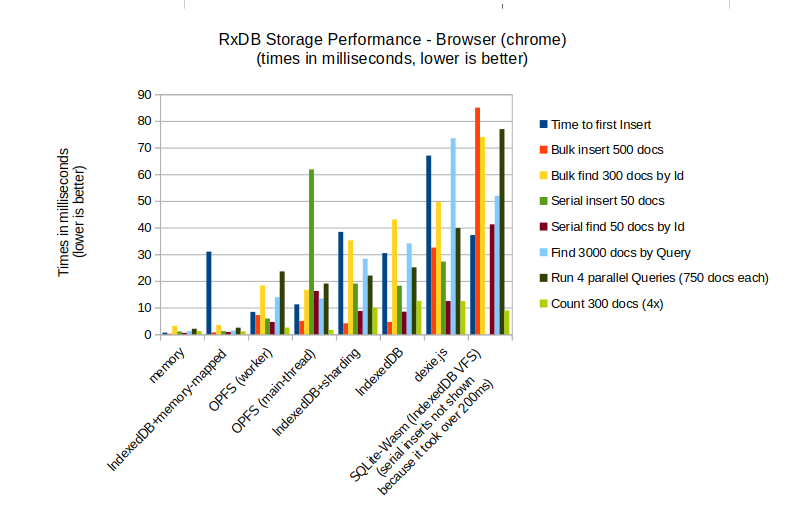
Performance comparison with other browser storages
Here is a performance overview of the various browser based storage implementation of RxDB:
Follow Up
Continue your deep dive into RxDB with official quickstart guides and star the repository on GitHub to stay updated.
-
RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with the RxDB Quickstart.
-
RxDB GitHub: Explore the source, open issues, and star ⭐ the project at RxDB GitHub Repo.
By combining IndexedDB's local storage with RxDB's powerful features, you can build performant, robust, and offline-capable Angular applications. RxDB takes care of the lower-level complexities, letting you focus on delivering a great user experience-online or off.
 Ask a question on the forums about Build Smarter...
Ask a question on the forums about Build Smarter...