RxDB as a Database for React Applications
In the rapidly evolving landscape of web development, React has emerged as a cornerstone technology for building dynamic and responsive user interfaces. With the increasing complexity of modern web applications, efficient data management becomes pivotal. This article delves into the integration of RxDB, a potent client-side database, with React applications to optimize data handling and elevate the overall user experience.
React has revolutionized the way web applications are built by introducing a component-based architecture. This approach enables developers to create reusable UI components that efficiently update in response to changes in data. The virtual DOM mechanism, a key feature of React, facilitates optimized rendering, enhancing performance and user interactivity.
While React excels at managing the user interface, the need for efficient data storage and retrieval mechanisms is equally significant. A client-side database brings several advantages to React applications:
- Improved Performance: Local data storage reduces the need for frequent server requests, resulting in faster data retrieval and enhanced application responsiveness.
- Offline Capabilities: A client-side database enables offline access to data, allowing users to interact with the application even when they are disconnected from the internet.
- Real-Time Updates: With the ability to observe changes in data, client-side databases facilitate real-time updates to the UI, ensuring users are always presented with the latest information.
- Reduced Server Load: By handling data operations locally, client-side databases alleviate the load on the server, contributing to a more scalable architecture.
Introducing RxDB as a JavaScript Database
RxDB, a powerful JavaScript database, has garnered attention as an optimal solution for managing data in React applications. Built on top of the IndexedDB standard, RxDB combines the principles of reactive programming with database management. Its core features include reactive data handling, offline-first capabilities, and robust data replication.
What is RxDB?
RxDB, short for Reactive Database, is an open-source JavaScript database that seamlessly integrates reactive programming with database operations. It offers a comprehensive API for performing database actions and synchronizing data across clients and servers. RxDB's underlying philosophy revolves around observables, allowing developers to reactively manage data changes and create dynamic user interfaces.
Reactive Data Handling
One of RxDB's standout features is its support for reactive data handling. Traditional databases often require manual intervention for data fetching and updating, leading to complex and error-prone code. RxDB, however, automatically notifies subscribers whenever data changes occur, eliminating the need for explicit data manipulation. This reactive approach simplifies code and enhances the responsiveness of React components.
Local-First Approach
RxDB embraces a local-first methodology, enabling applications to function seamlessly even in offline scenarios. By storing data locally, RxDB ensures that users can interact with the application and make updates regardless of internet connectivity. Once the connection is reestablished, RxDB synchronizes the local changes with the remote database, maintaining data consistency across devices.
Data Replication
Data replication is a cornerstone of modern applications that require synchronization between multiple clients and servers. RxDB provides robust data replication mechanisms that facilitate real-time synchronization between different instances of the database. This ensures that changes made on one client are promptly propagated to others, contributing to a cohesive and unified user experience.
Observable Queries
RxDB extends the concept of observables beyond data changes. It introduces observable queries, allowing developers to observe the results of database queries. This feature enables automatic updates to query results whenever relevant data changes occur. Observable queries simplify state management by eliminating the need to manually trigger updates in response to changing data.
await db.heroes.find({
selector: {
healthpoints: {
$gt: 0
}
}
})
.$ // the $ returns an observable that emits each time the result set of the query changes
.subscribe(aliveHeroes => console.dir(aliveHeroes));Multi-Tab Support
Web applications often operate in multiple browser tabs or windows. RxDB accommodates this scenario by offering built-in multi-tab support. It ensures that data changes made in one tab are efficiently propagated to other tabs, maintaining data consistency and providing a seamless experience for users interacting with the application across different tabs.
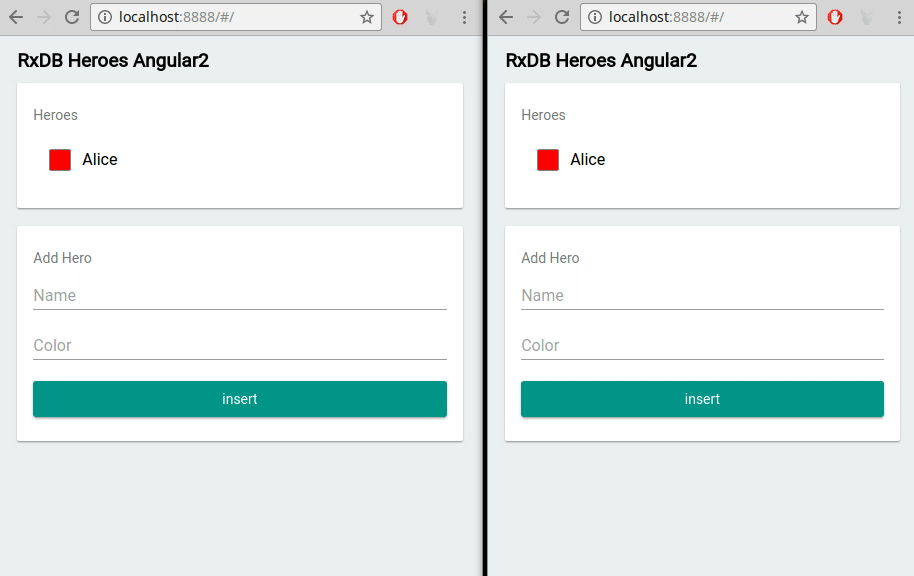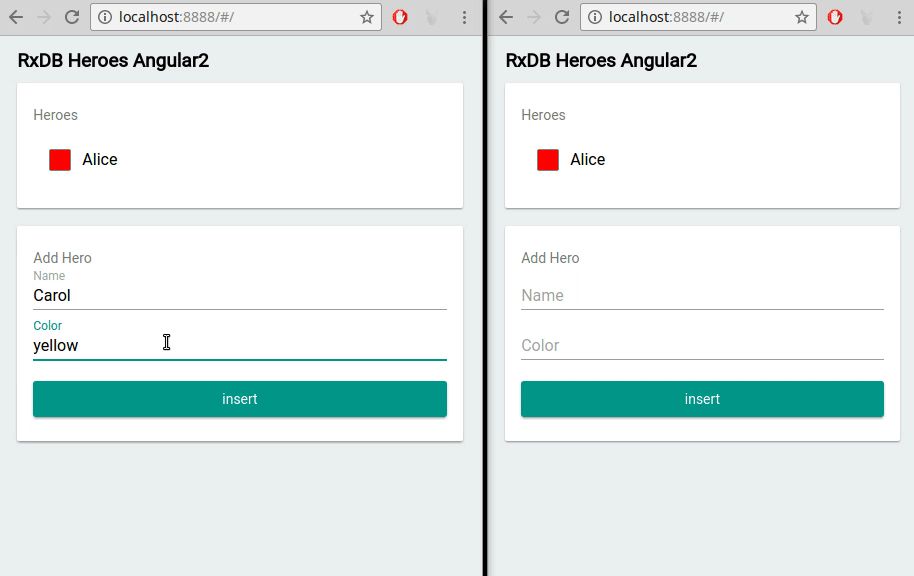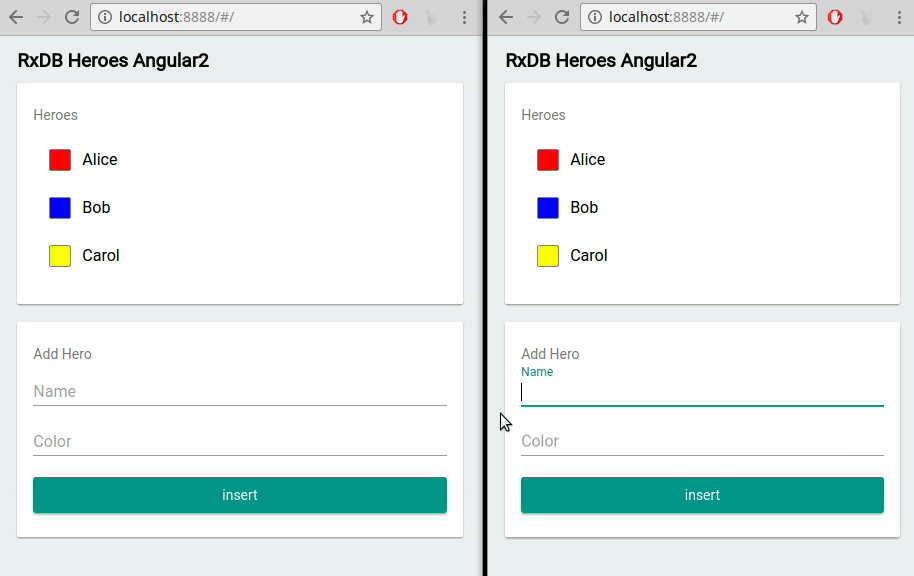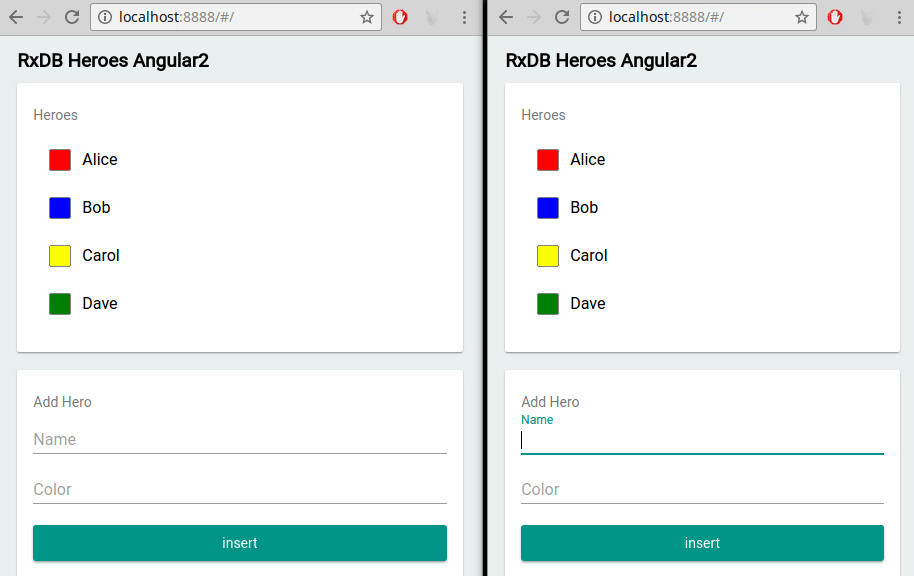
RxDB vs. Other React Database Options
While considering database options for React applications, RxDB stands out due to its unique combination of reactive programming and database capabilities. Unlike traditional solutions such as IndexedDB or Web Storage, which provide basic data storage, RxDB offers a dedicated database solution with advanced features. Additionally, while state management libraries like Redux and MobX can be adapted for database use, RxDB provides an integrated solution specifically designed for handling data.
IndexedDB in React and the Advantage of RxDB
Using IndexedDB directly in React can be challenging due to its low-level, callback-based API which doesn't align neatly with modern React's Promise and async/await patterns. This intricacy often leads to bulky and complex implementations for developers. Also, when used wrong, IndexedDB can have a worse performance profile than it could have. In contrast, RxDB, with the IndexedDB RxStorage and the LocalStorage RxStorage, abstracts these complexities, integrating reactive programming and providing a more streamlined experience for data management in React applications. Thus, RxDB offers a more intuitive approach, eliminating much of the manual overhead required with IndexedDB.
Using RxDB in a React Application
The process of integrating RxDB into a React application is straightforward. Begin by installing RxDB as a dependency:
npm install rxdb rxjs
Once installed, RxDB can be imported and initialized within your React components. The following code snippet illustrates a basic setup:
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'heroesdb', // <- name
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage(), // <- RxStorage
password: 'myPassword', // <- password (optional)
multiInstance: true, // <- multiInstance (optional, default: true)
eventReduce: true, // <- eventReduce (optional, default: false)
cleanupPolicy: {} // <- custom cleanup policy (optional)
});Using RxDB React Hooks
The rxdb-hooks package provides a set of React hooks that simplify data management within components. These hooks leverage RxDB's reactivity to automatically update components when data changes occur. The following example demonstrates the usage of the useRxCollection and useRxQuery hooks to query and observe a collection:
const collection = useRxCollection('characters');
const query = collection.find().where('affiliation').equals('Jedi');
const {
result: characters,
isFetching,
fetchMore,
isExhausted,
} = useRxQuery(query, {
pageSize: 5,
pagination: 'Infinite',
});
if (isFetching) {
return 'Loading...';
}
return (
<CharacterList>
{characters.map((character, index) => (
<Character character={character} key={index} />
))}
{!isExhausted && <button onClick={fetchMore}>load more</button>}
</CharacterList>
);Different RxStorage Layers for RxDB
RxDB offers multiple storage layers, each backed by a different underlying technology. Developers can choose the storage layer that best suits their application's requirements. Some available options include:
- LocalStorage RxStorage: Built on top of the browser's LocalStorage API.
- IndexedDB RxStorage: The default RxDB storage layer, providing efficient data storage in modern browsers.
- OPFS RxStorage: Uses the Origin Private File System (OPFS) for storage, suitable for Electron applications.
- Memory RxStorage: Stores data in memory, primarily intended for testing and development purposes.
- SQLite RxStorage: Stores data in an SQLite database. Can be used in a browser with React by using a SQLite database that was compiled to WebAssembly. Using SQLite in React might not be the best idea, because a compiled SQLite wasm file is about one megabyte of code that has to be loaded and rendered by your users. Using native browser APIs like IndexedDB and OPFS have shown to be a more optimal database solution for browser based React apps compared to SQLite.
Synchronizing Data with RxDB between Clients and Servers
The offline-first approach is a fundamental principle of RxDB's design. When dealing with client-server synchronization, RxDB ensures that changes made offline are captured and propagated to the server once connectivity is reestablished. This mechanism guarantees that data remains consistent across different client instances, even when operating in an occasionally connected environment.
RxDB offers a range of replication plugins that facilitate data synchronization between clients and servers. These plugins support various synchronization strategies, such as one-way replication, two-way replication, and custom conflict resolution. Developers can select the appropriate plugin based on their application's synchronization requirements.
Advanced RxDB Features and Techniques
Encryption of Local Data Security is paramount when handling sensitive user data. RxDB supports data encryption, ensuring that locally stored information remains protected from unauthorized access. This feature is particularly valuable when dealing with sensitive data in offline scenarios.
Indexing and Performance Optimization
Efficient indexing is critical for achieving optimal database performance. RxDB provides mechanisms to define indexes on specific fields, enhancing query speed and reducing the computational overhead of data retrieval.
JSON Key Compression
RxDB employs JSON key compression to reduce storage space and improve performance. This technique minimizes the memory footprint of the database, making it suitable for applications with limited resources.
Change Streams and Event Handling
RxDB enables developers to subscribe to change streams, which emit events whenever data changes occur. This functionality facilitates real-time event handling and provides opportunities for implementing features such as notifications and live updates.
Conclusion
In the realm of React application development, efficient data management is pivotal to delivering a seamless and engaging user experience. RxDB emerges as a compelling solution, seamlessly integrating reactive programming principles with sophisticated database capabilities. By adopting RxDB, React developers can harness its powerful features, including reactive data handling, offline-first support, and real-time synchronization. With RxDB as a foundational pillar, React applications can excel in responsiveness, scalability, and data integrity. As the landscape of web development continues to evolve, RxDB remains a steadfast companion for creating robust and dynamic React applications.
Follow Up
To explore more about RxDB and leverage its capabilities for browser database development, check out the following resources:
- RxDB GitHub Repository: Visit the official GitHub repository of RxDB to access the source code, documentation, and community support.
- RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with RxDB by following the provided quickstart guide, which provides step-by-step instructions for setting up and using RxDB in your projects.
- RxDB React Example at GitHub
 Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database for...
Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database for...