What is a realtime database?
I have been building RxDB, a NoSQL realtime JavaScript database for many years. Often people get confused by the word realtime database, because the word realtime is so vaguely defined that it can mean everything and nothing at the same time.
In this article we will explore what a realtime database is, and more important, what it is not.
Realtime as in realtime computing
When "normal" developers hear the word "realtime", they think of Real-time computing (RTC). Real-time computing is a type of computer processing that guarantees specific response times for tasks or events, crucial in applications like industrial control, automotive systems, and aerospace. It relies on specialized operating systems (RTOS) to ensure predictability and low latency. Hard real-time systems must never miss deadlines, while soft real-time systems can tolerate occasional delays. Real-time responses are often understood to be in the order of milliseconds, and sometimes microseconds.
Consider the role of real-time computing in car airbags: sensors detect collision force, swiftly process the data, and immediately decide to deploy the airbags within milliseconds. Such rapid action is imperative for safeguarding passengers. Hence, the controlling chip must guarantee a certain response time - it must operate in "realtime".
But when people talk about realtime databases, especially in the web-development world, they almost never mean realtime, as in realtime computing, they mean something else. In fact, with any programming language that run on end users devices, it is not even possible to built a "real" realtime database. A program, like a JavaScript (browser or Node.js) process, can be halted by the operating systems task manager at any time and therefore it will never be able to guarantee specific response times. To build a realtime computing database, you would need a realtime capable operating system.
Real time Database as in realtime replication
When talking about realtime databases, most people refer to realtime, as in realtime replication. Often they mean a very specific product which is the Firebase Realtime Database (not the Firestore).
In the context of the Firebase Realtime Database, "realtime" means that data changes are synchronized and delivered to all connected clients or devices as soon as they occur, typically within milliseconds. This means that when any client updates, adds, or removes data in the database, all other clients that are connected to the same database instance receive those updates instantly, without the need for manual polling or frequent HTTP requests.
In short, when replicating data between databases, instead of polling, we use a websocket connection to live-stream all changes between the server and the clients, this is labeled as "realtime database". A similar thing can be done with RxDB and the RxDB Replication Plugins.
Realtime as in realtime applications
In the context of realtime client-side applications, "realtime" refers to the immediate or near-instantaneous processing and response to events or data inputs. When data changes, the application must directly update to reflect the new data state, without any user interaction or delay. Notice that the change to the data could have come from any source, like a user action, an operation in another browser tab, or even an operation from another device that has been replicated to the client.
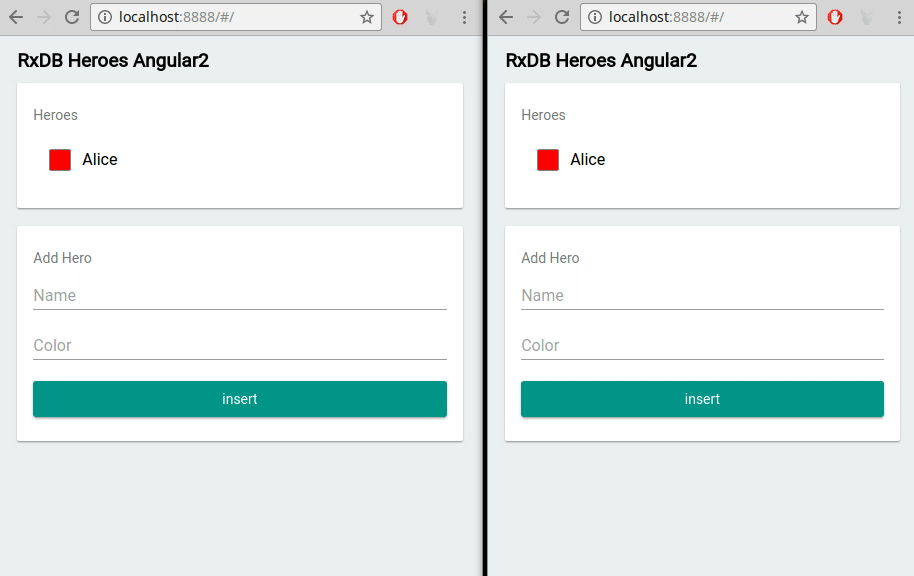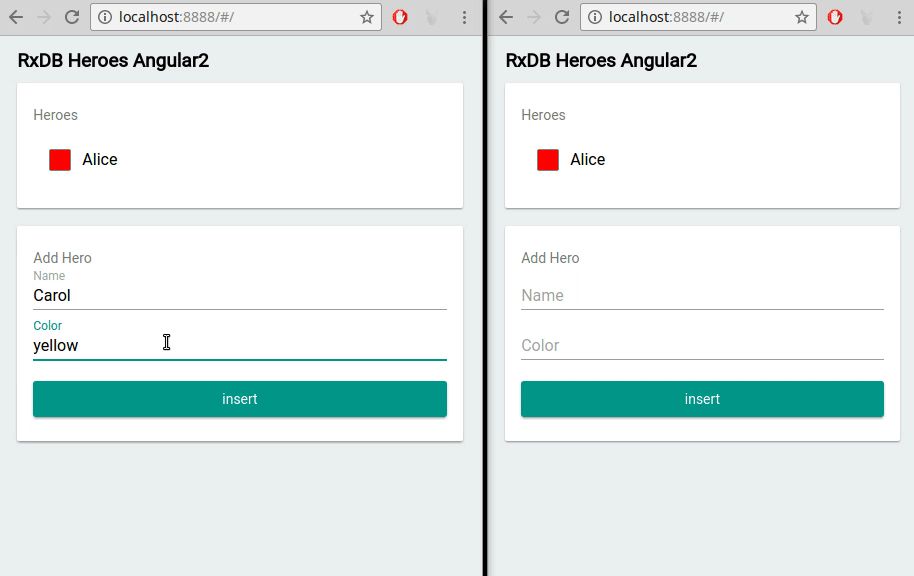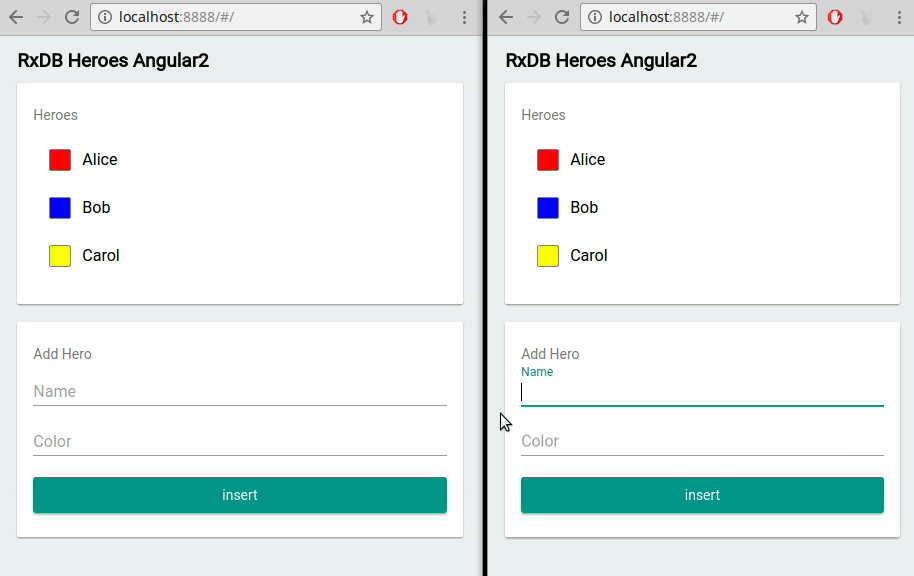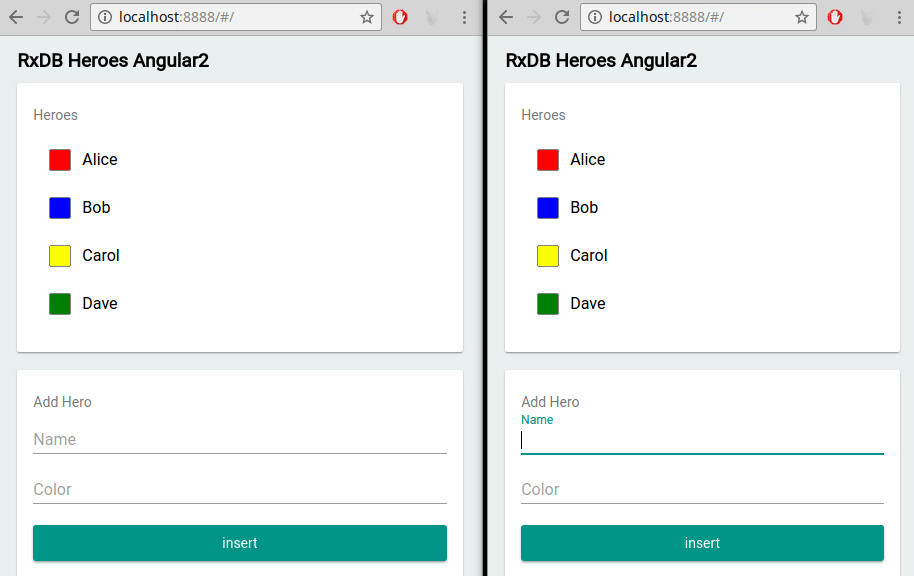
In contrast to push-pull based databases (e.g., MySQL or MongoDB servers), a realtime database contains features which make it easy to build realtime applications. For example with RxDB you can not only fetch query results once, but instead you can subscribe to a query and directly update the HTML dom tree whenever the query has a new result set:
await db.heroes.find({
selector: {
healthpoints: {
$gt: 0
}
}
})
.$ // The $ returns an observable that emits whenever the query's result set changes.
.subscribe(aliveHeroes => {
// Refresh the HTML list each time there are new query results.
const newContent = aliveHeroes.map(doc => '<li>' + doc.name + '</li>');
document.getElementById('#myList').innerHTML = newContent;
});
// You can even subscribe to any RxDB document's fields.
myDocument.firstName$.subscribe(newName => console.log('name is: ' + newName));A competent realtime application is engineered to offer feedback or results swiftly, ideally within milliseconds to microseconds. Ideally, a data modification should be processed in under 16 milliseconds (since 1 second divided by 60 frames equals 16.66ms) to ensure users don't perceive any lag from input to visualization. RxDB utilizes the EventReduce algorithm to manage changes more swiftly than 16ms. However, it can never assure fixed response times as a "realtime computing database" would.
Follow Up
- Dive into the RxDB Quickstart
- Discover more about the RxDB realtime Sync Engine
- Join the conversation at RxDB Chat
 Ask a question on the forums about What is a realtime...
Ask a question on the forums about What is a realtime...