RxDB as a Database in a jQuery Application
In the early days of dynamic web development, jQuery emerged as a popular library that simplified DOM manipulation and AJAX requests. Despite the rise of modern frameworks, many developers still maintain or extend existing jQuery projects, or leverage jQuery in specific contexts. As jQuery applications grow in complexity, they often require efficient data handling, offline support, and synchronization capabilities. This is where RxDB, a reactive JavaScript database for the browser, node.js, and mobile devices, steps in.
jQuery Web Applications
jQuery provides a simple API for DOM manipulation, event handling, and AJAX calls. It has been widely adopted due to its ease of use and strong community support. Many projects continue to rely on jQuery for handling client-side functionality, UI interactions, and animations. As these applications evolve, the need for a robust database solution that can manage data locally (and offline) becomes increasingly important.
Importance of Databases in jQuery Applications
Modern, data-driven jQuery applications often need to:
- Store and retrieve data locally for quick and responsive user experiences.
- Synchronize data between clients or with a central server.
- Handle offline scenarios seamlessly.
- Handle large or complex data structures without repeatedly hitting the server.
Relying solely on server endpoints or basic browser storage (like localStorage) can quickly become unwieldy for larger or more complex use cases. Enter RxDB, a dedicated solution that manages data on the client side while offering real-time synchronization and offline-first capabilities.
Introducing RxDB as a Database Solution
RxDB (short for Reactive Database) is built on top of IndexedDB and leverages RxJS to provide a modern, reactive approach to handling data in the browser. With RxDB, you can store documents locally, query them in real-time, and synchronize changes with a remote server whenever an internet connection is available.
Key Features
- Reactive Data Handling: RxDB emits real-time updates whenever your data changes, allowing you to instantly reflect these changes in the DOM with jQuery.
- Offline-First Approach: Keep your application usable even when the user's network is unavailable. Data is automatically synchronized once connectivity is restored.
- Data Replication: Enable multi-device or multi-tab synchronization with minimal effort.
- Observable Queries: Reduce code complexity by subscribing to queries instead of constantly polling for changes.
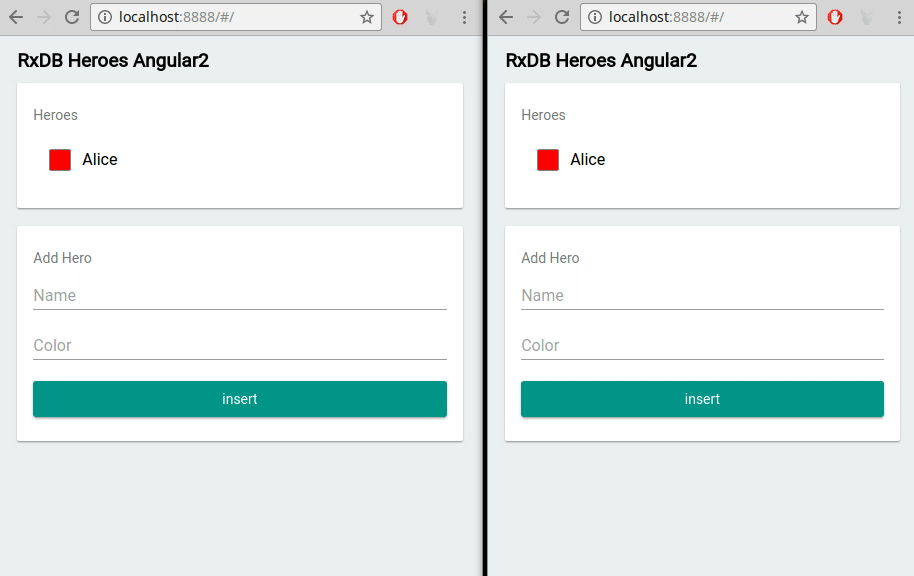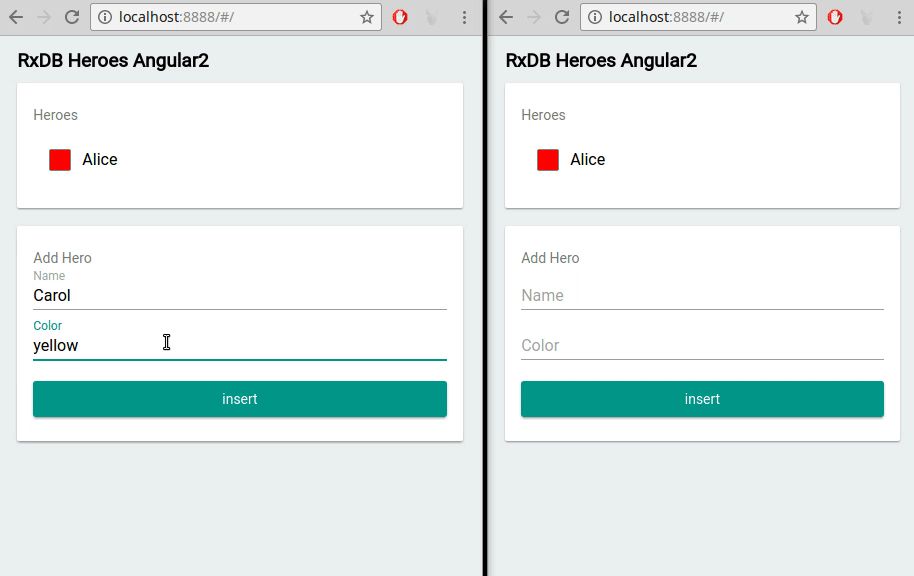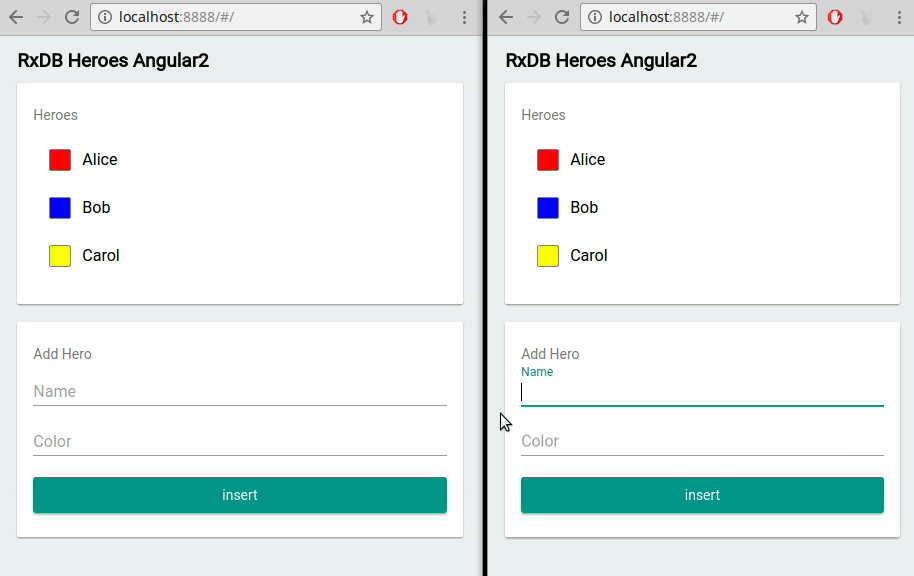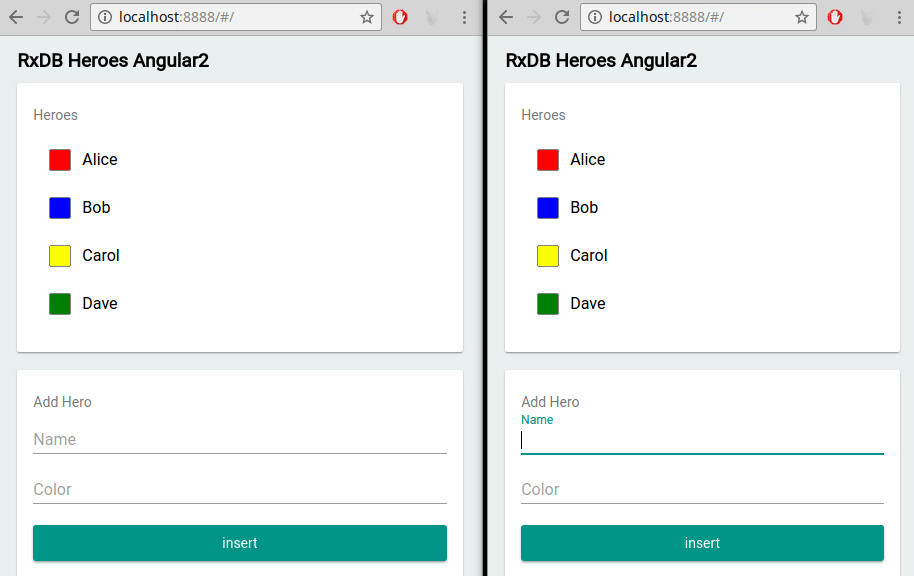
- Multi-Tab Support: If a user opens your jQuery application in multiple tabs, RxDB keeps data in sync across all sessions.
Getting Started with RxDB
What is RxDB?
RxDB is a client-side NoSQL database that stores data in the browser (or node.js) and synchronizes changes with other instances or servers. Its design embraces reactive programming principles, making it well-suited for real-time applications, offline scenarios, and multi-tab use cases.
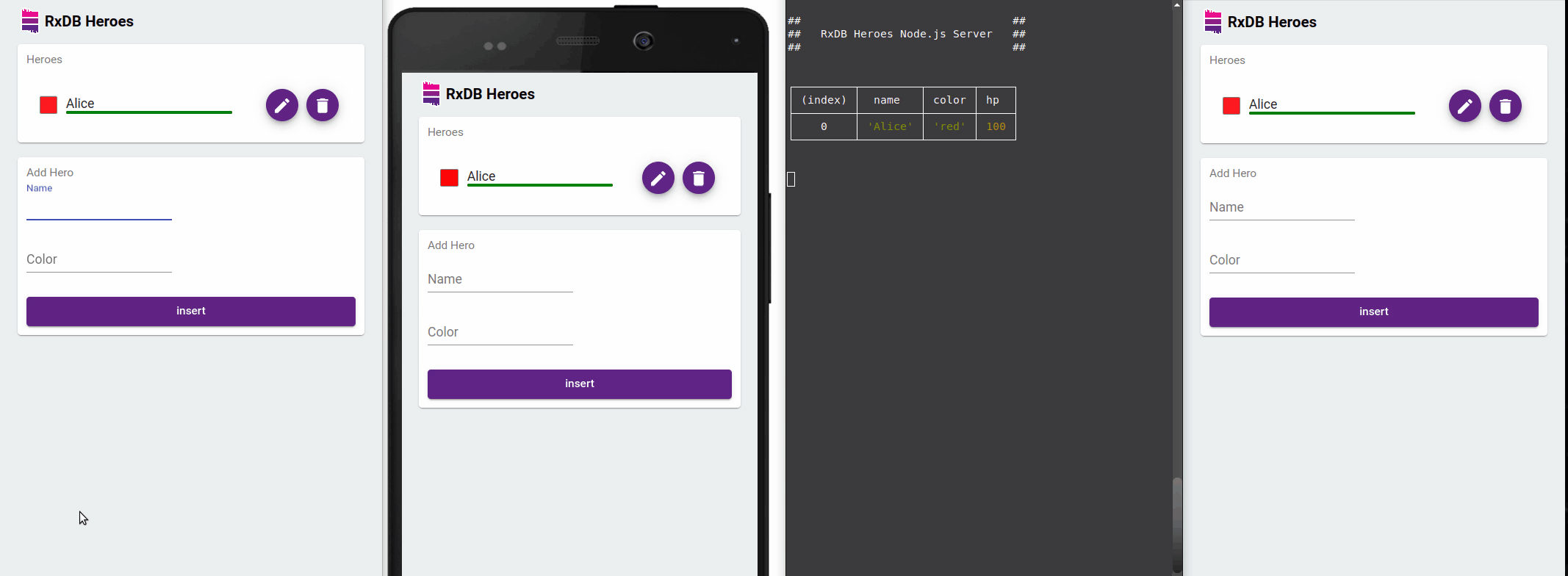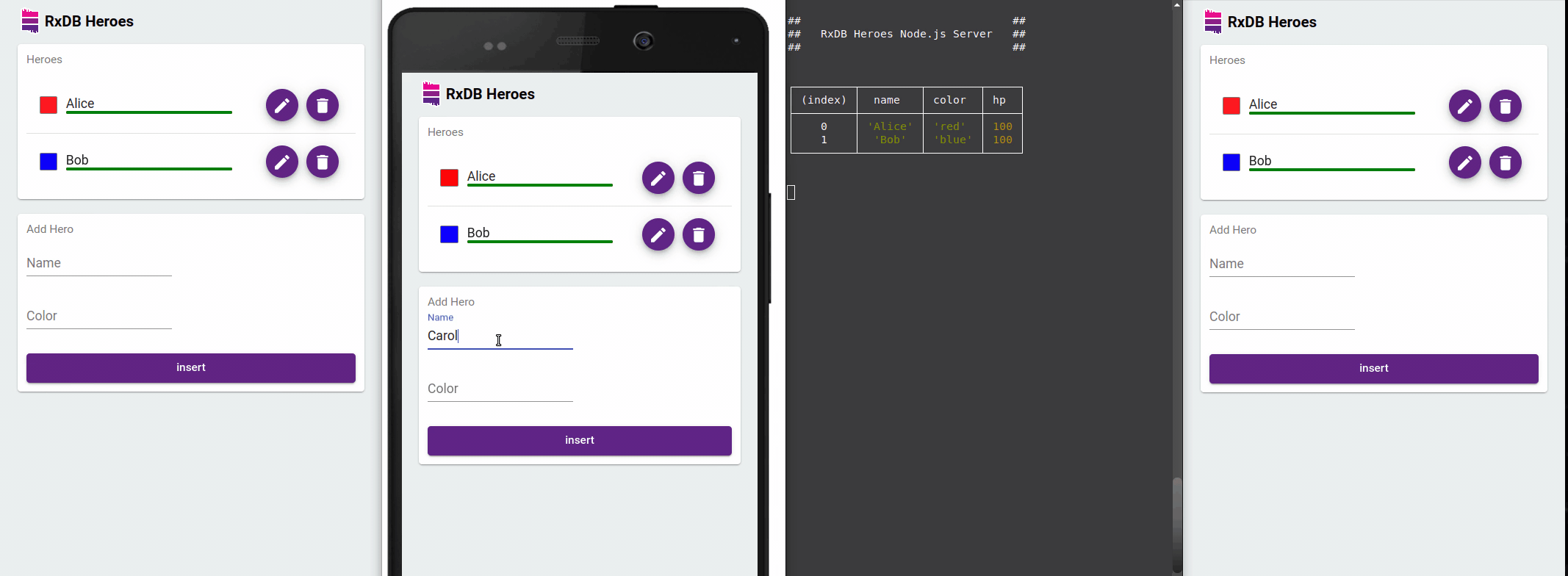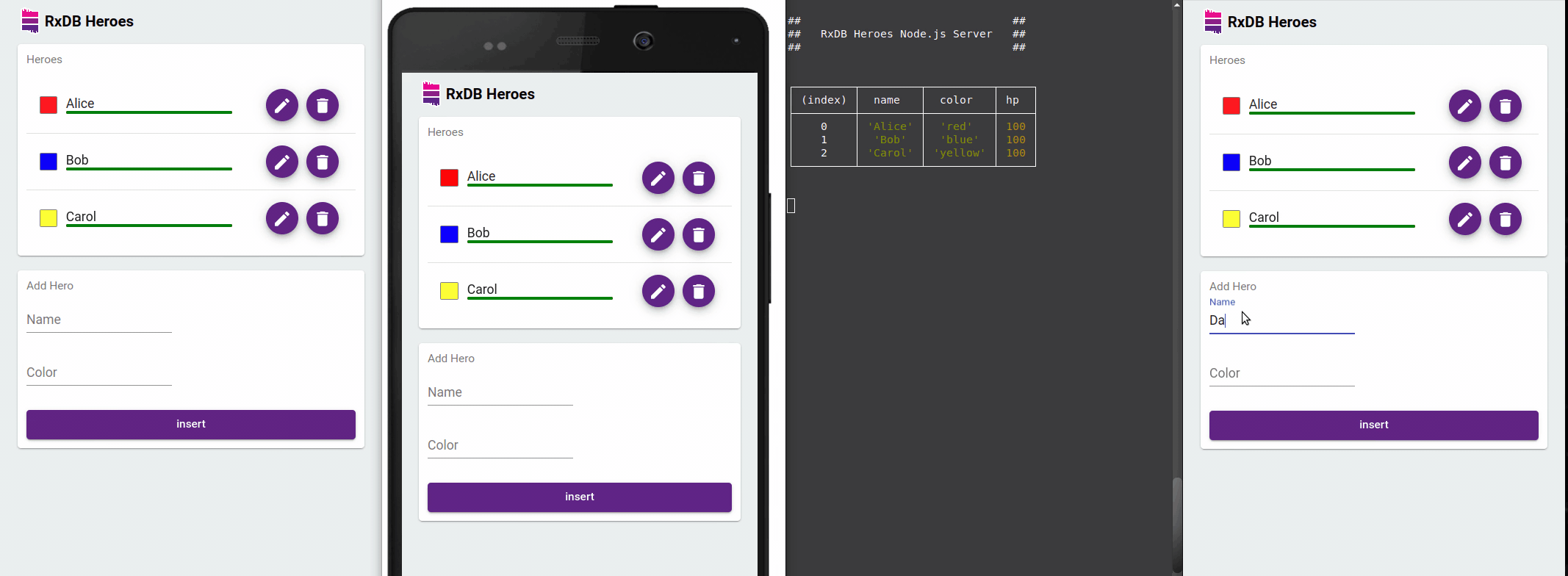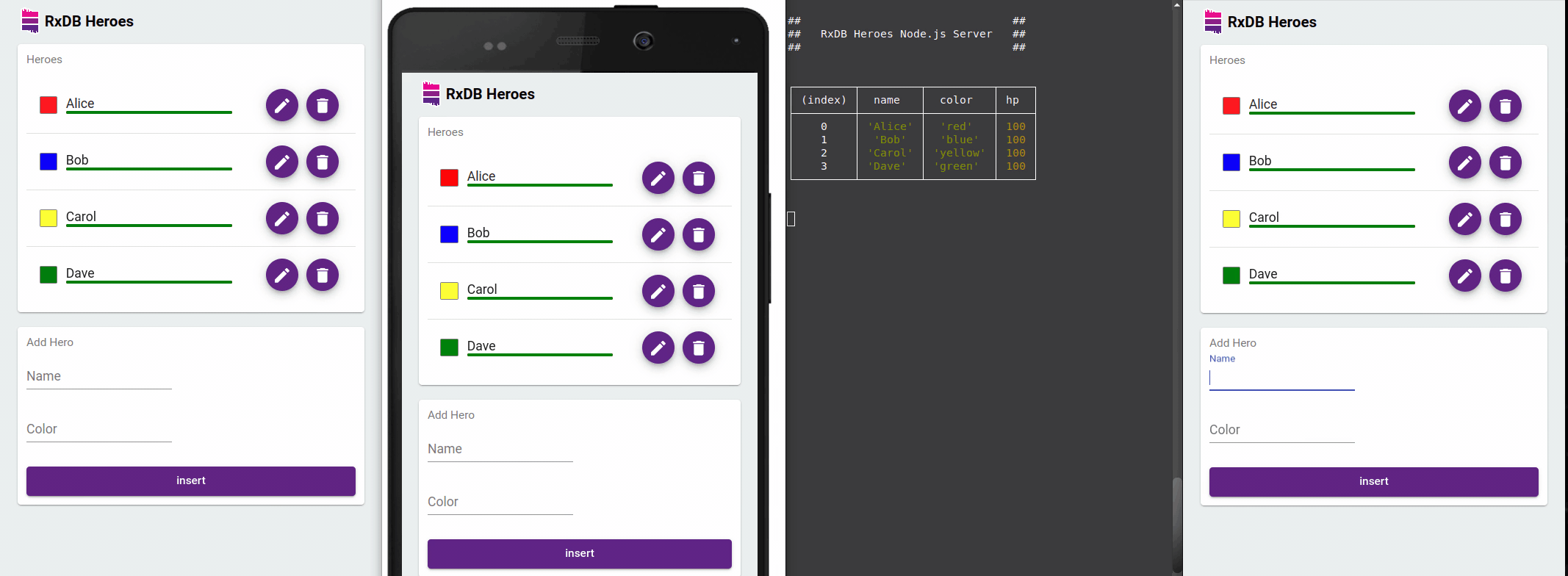
Reactive Data Handling
RxDB's use of observables enables an event-driven architecture where data mutations automatically trigger UI updates. In a jQuery application, you can subscribe to these changes and update DOM elements as soon as data changes occur - no need for manual refresh or complicated change detection logic.
Offline-First Approach
One of RxDB's distinguishing traits is its emphasis on offline-first design. This means your jQuery application continues to function, display, and update data even when there's no network connection. When connectivity is restored, RxDB synchronizes updates with the server or other peers, ensuring consistency across all instances.
Data Replication
RxDB supports real-time data replication with different backends. By enabling replication, you ensure that multiple clients - be they multiple browser tabs or separate devices - stay in sync. RxDB's conflict resolution strategies help keep the data consistent even when multiple users make changes simultaneously.
Observable Queries
Instead of static queries, RxDB provides observable queries. Whenever data relevant to a query changes, RxDB re-emits the new result set. You can subscribe to these updates within your jQuery code and instantly reflect them in the UI.
Multi-Tab Support
Running your jQuery app in multiple tabs? RxDB automatically synchronizes changes between those tabs. Users can freely switch windows without missing real-time updates.
RxDB vs. Other jQuery Database Options
Historically, jQuery developers might use localStorage or raw IndexedDB for storing data. However, these solutions can require significant boilerplate, lack reactivity, and offer no built-in sync or conflict resolution. RxDB fills these gaps with an out-of-the-box solution, abstracting away low-level database complexities and providing an event-driven, offline-capable approach.
Using RxDB in a jQuery Application
Installing RxDB
Install RxDB (and rxjs) via npm or yarn:
npm install rxdb rxjsIf your project isn't set up with a build process, you can still use bundlers like Webpack or Rollup, or serve RxDB as a UMD bundle. Once included, you'll have access to RxDB globally or via import statements.
Creating and Configuring a Database
Below is a minimal example of how to create an RxDB instance and collection. You can call this when your page initializes, then store the db object for later use:
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
async function initDatabase() {
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'heroesdb',
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage(),
password: 'myPassword', // optional encryption password
multiInstance: true, // multi-tab support
eventReduce: true // optimizes event handling
});
await db.addCollections({
hero: {
schema: {
title: 'hero schema',
version: 0,
primaryKey: 'id',
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: { type: 'string' },
name: { type: 'string' },
points: { type: 'number' }
}
}
}
});
return db;
}Updating the DOM with jQuery
Once you have your RxDB instance, you can query data reactively and use jQuery to manipulate the DOM:
// Example: Displaying heroes using jQuery
$(document).ready(async function () {
const db = await initDatabase();
// Subscribing to all hero documents
db.hero
.find()
.$ // the observable
.subscribe((heroes) => {
// Clear the list
$('#heroList').empty();
// Append each hero to the DOM
heroes.forEach((hero) => {
$('#heroList').append(`
<li>
<strong>${hero.name}</strong> - Points: ${hero.points}
</li>
`);
});
});
// Example of adding a new hero
$('#addHeroBtn').on('click', async () => {
const heroName = $('#heroName').val();
const heroPoints = parseInt($('#heroPoints').val(), 10);
await db.hero.insert({
id: Date.now().toString(),
name: heroName,
points: heroPoints
});
});
});With this approach, any time data in the hero collection changes - like when a new hero is added - your jQuery code re-renders the list of heroes automatically.
Different RxStorage layers for RxDB
RxDB supports multiple storage backends (RxStorage layers). Some popular ones:
- LocalStorage.js RxStorage: Uses the browsers localstorage. Fast and easy to set up.
- IndexedDB RxStorage: Direct IndexedDB usage, suitable for modern browsers.
- OPFS RxStorage: Uses the File System Access API for better performance in supported browsers.
- Memory RxStorage: Stores data in memory, handy for tests or ephemeral data.
- SQLite RxStorage: Uses SQLite (potentially via WebAssembly). In typical browser-based scenarios, localstorage or IndexedDB storage is usually more straightforward.
Synchronizing Data with RxDB between Clients and Servers
Offline-First Approach
RxDB's offline-first approach allows your jQuery application to store and query data locally. Users can continue interacting, even offline. When connectivity returns, RxDB syncs to the server.
Conflict Resolution
Should multiple clients update the same document, RxDB offers conflict handling strategies. You decide how to resolve conflicts - like keeping the latest edit or merging changes - ensuring data integrity across distributed systems.
Bidirectional Synchronization
With RxDB, data changes flow both ways: from client to server and from server to client. This real-time synchronization ensures that all users or tabs see consistent, up-to-date data.
Advanced RxDB Features and Techniques
Indexing and Performance Optimization
Create indexes on frequently queried fields to speed up performance. For large data sets, indexing can drastically improve query times, keeping your jQuery UI snappy.
Encryption of Local Data
RxDB supports encryption to secure data stored in the browser. This is crucial if your application handles sensitive user information.
Change Streams and Event Handling
Use change streams to listen for data modifications at the database or collection level. This can trigger real-time UI updates, notifications, or custom logic whenever the data changes.
JSON Key Compression
If your data model has large or repetitive field names, JSON key compression can minimize stored document size and potentially boost performance.
Best Practices for Using RxDB in jQuery Applications
- Centralize Your Database: Initialize and configure RxDB in one place. Expose the instance where needed or store it globally to avoid re-creating it on every script.
- Leverage Observables: Instead of polling or manually refreshing data, rely on RxDB's reactivity. Subscribe to queries and let RxDB inform you when data changes.
- Handle Subscriptions: If you create subscriptions in a single-page context, ensure you don't re-subscribe endlessly or create memory leaks. Clean them up if you're navigating away or removing DOM elements.
- Offline Testing: Thoroughly test how your jQuery app behaves without a network connection. Simulate offline states in your browser's dev tools or with flight mode to ensure the user experience remains smooth.
- Performance Profiling: For large data sets or frequent data updates, add indexes and carefully measure query performance. Optimize only where needed.
Follow Up
To explore more about RxDB and leverage its capabilities for browser database development, check out the following resources:
- RxDB GitHub Repository: Visit the official GitHub repository of RxDB to access the source code, documentation, and community support.
- RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with RxDB by following the provided quickstart guide, which offers step-by-step instructions for setting up and using RxDB in your projects.
- RxDB Examples: Browse official examples to see RxDB in action and learn best practices you can apply to your own project - even if jQuery isn't explicitly featured, the patterns are similar.

 Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...
Ask a question on the forums about RxDB as a Database in...