Browser Storage - RxDB as a Database for Browsers
Storing Data in the Browser
When it comes to building web applications, one essential aspect is the storage of data. Two common methods of storing data directly within the user's web browser are LocalStorage and IndexedDB. These browser-based storage options serve various purposes and cater to different needs in web development.
LocalStorage
LocalStorage is a straightforward way to store small amounts of data in the user's web browser. It operates on a simple key-value basis and is relatively easy to use. While it has limitations, it is suitable for basic data storage requirements.
IndexedDB
IndexedDB, on the other hand, offers a more robust and structured approach to browser-based data storage. It can handle larger datasets and complex queries, making it a valuable choice for more advanced web applications.
Why Store Data in the Browser
Now that we've explored the methods of storing data in the browser, let's delve into why this is a beneficial strategy for web developers:
-
Caching: Storing data in the browser allows you to cache frequently used information. This means that your web application can access essential data more quickly because it doesn't need to repeatedly fetch it from a server. This results in a smoother and more responsive user experience.
-
Offline Access: One significant advantage of browser storage is that data becomes portable and remains accessible even when the user is offline. This feature ensures that users can continue to use your application, view their saved information, and make changes, irrespective of their internet connection status.
-
Faster Real-time Applications: For real-time applications, having data stored locally in the browser significantly enhances performance. Local data allows your application to respond faster to user interactions, creating a more seamless and responsive user interface.
-
Low-Latency Queries: When you run queries locally within the browser, you minimize the latency associated with network requests. This results in near-instant access to data, which is particularly crucial for applications that require rapid data retrieval.
-
Faster Initial Application Start Time: By preloading essential data into browser storage, you can reduce the initial load time of your web application. Users can start using your application more swiftly, which is essential for making a positive first impression.
-
Store Local Data with Encryption: For applications that deal with sensitive data, browser storage allows you to implement encryption to secure the stored information. This ensures that even if data is stored on the user's device, it remains confidential and protected.
In summary, storing data in the browser offers several advantages, including improved performance, offline access, and enhanced user experiences. LocalStorage and IndexedDB are two valuable tools that developers can utilize to leverage these benefits and create web applications that are more responsive and user-friendly.
Browser Storage Limitations
While browser storage, such as LocalStorage and IndexedDB, offers many advantages, it's important to be aware of its limitations:
-
Slower Performance Compared to Native Databases: Browser-based storage solutions can't match the performance of native server-side databases. They may experience slower data retrieval and processing, especially for large datasets or complex operations.
-
Storage Space Limitations: Browsers impose restrictions on the amount of data that can be stored locally. This limitation can be problematic for applications with extensive data storage requirements, potentially necessitating creative solutions to manage data effectively.
Why SQL Databases Like SQLite Aren't a Good Fit for the Browser
SQL databases like SQLite, while powerful in server environments, may not be the best choice for browser-based applications due to various reasons:
Push/Pull Based vs. Reactive
SQL databases often use a push/pull model for data synchronization. This approach is less reactive and may not align well with the real-time nature of web applications, where immediate updates to the user interface are crucial.
Build Size of Server-Side Databases
Server-side databases like SQLite have a significant build size, which can increase the initial load time of web applications. This can result in a suboptimal user experience, particularly for users with slower internet connections.
Initialization Time and Performance
SQL databases are optimized for server environments, and their initialization processes and performance characteristics may not align with the needs of web applications. They might not offer the swift performance required for seamless user interactions.
Why RxDB Is a Good Fit as Browser Storage
RxDB is an excellent choice for browser-based storage due to its numerous features and advantages:
Flexible Storage Layer for Various Platforms
RxDB offers a flexible storage layer that can seamlessly integrate with different platforms, making it versatile and adaptable to various application needs.
NoSQL JSON Documents Are a Better Fit for UIs
NoSQL JSON documents, used by RxDB, are well-suited for user interfaces. They provide a natural and efficient way to structure and display data in web applications.
NoSQL Has Better TypeScript Support Compared to SQL
RxDB boasts robust TypeScript support, which is beneficial for developers who prefer type safety and code predictability in their projects.
Observable Document Fields
RxDB enables developers to observe individual document fields, offering fine-grained control over data tracking and updates.
Made in JavaScript, Optimized for JavaScript Applications
Being built in JavaScript and optimized for JavaScript applications, RxDB seamlessly integrates into web development stacks, minimizing compatibility issues.
Observable Queries (rxjs) to Automatically Update the UI on Changes
RxDB's support for Observable Queries allows the user interface to update automatically in real-time when data changes. This reactivity enhances the user experience and simplifies UI development.
const query = myCollection.find({
selector: {
age: {
$gt: 21
}
}
});
const querySub = query.$.subscribe(results => {
console.log('got results: ' + results.length);
});Optimized Observed Queries with the EventReduce Algorithm
RxDB's EventReduce Algorithm ensures efficient data handling and rendering, improving overall performance and responsiveness.
Handling of Schema Changes
RxDB provides built-in support for handling schema changes, simplifying database management when updates are required.
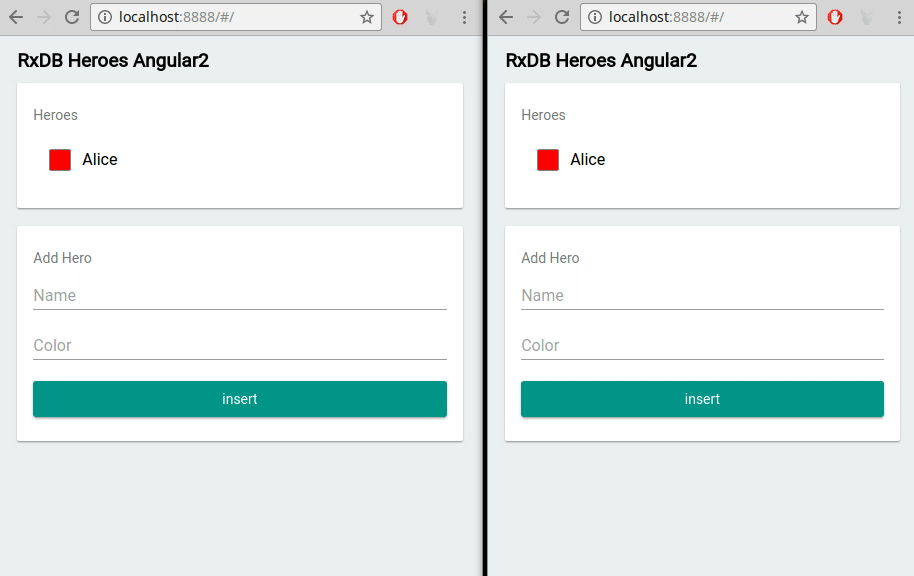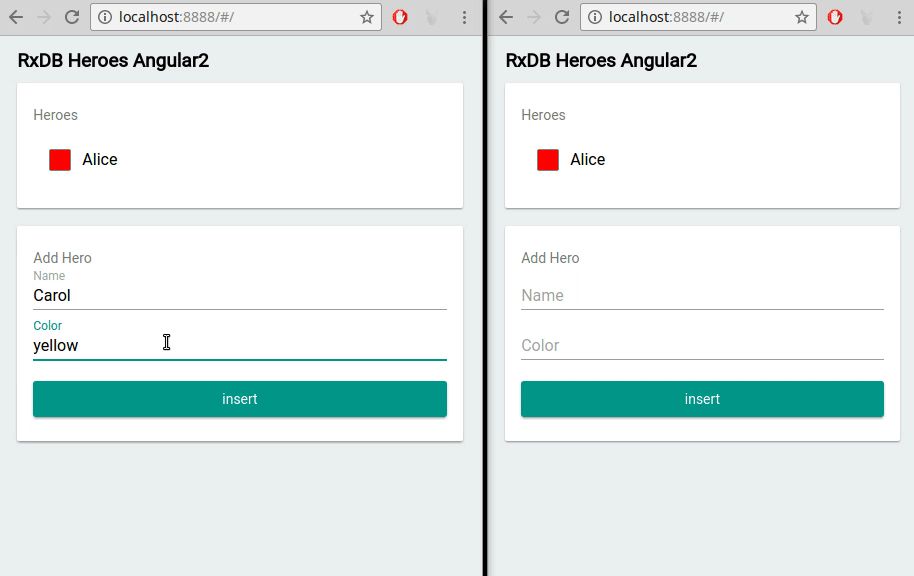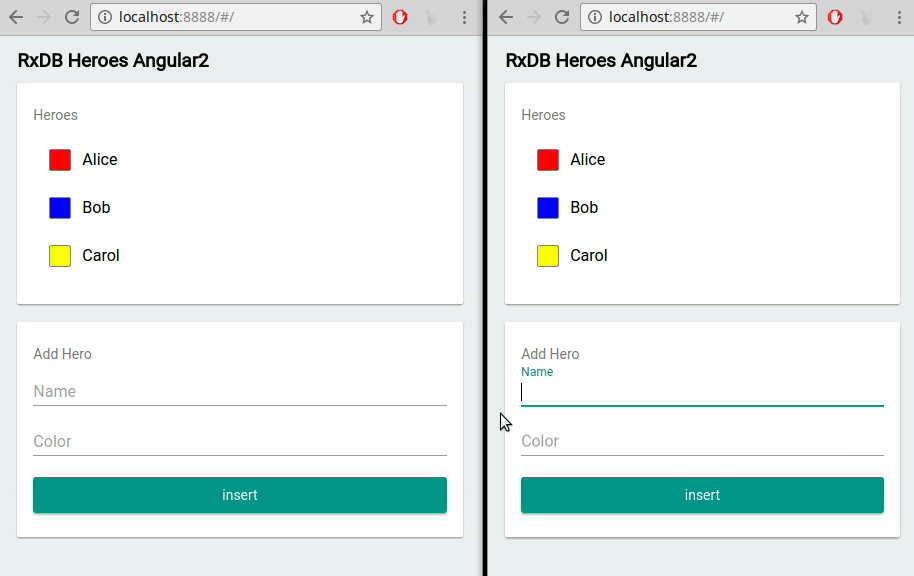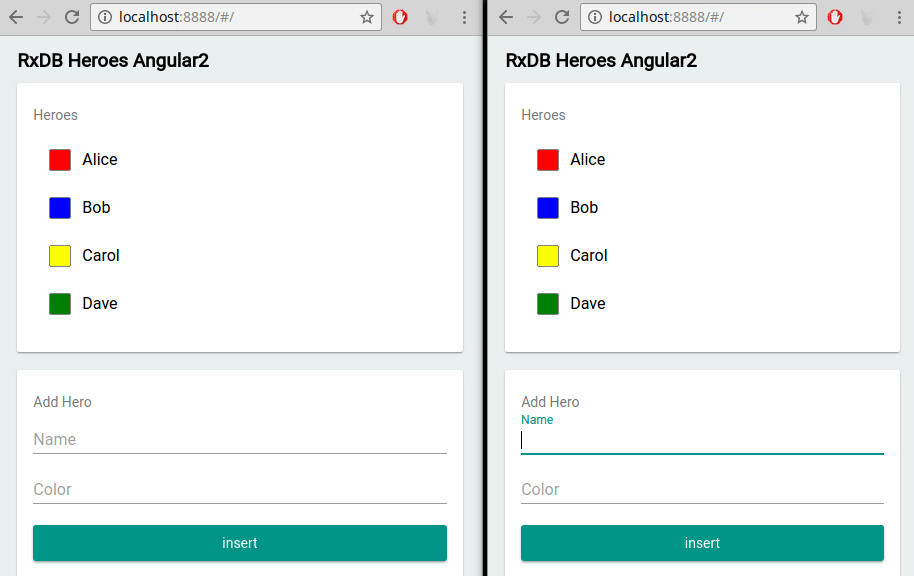
Built-In Multi-Tab Support
For applications requiring multi-tab support, RxDB natively handles data consistency across different browser tabs, streamlining data synchronization.
Storing Documents Compressed
Efficient data storage is achieved through document compression, reducing storage space requirements and enhancing overall performance.
Replication Algorithm for Compatibility with Any Backend
RxDB's Replication Algorithm facilitates compatibility with various backend systems, ensuring seamless data synchronization between the browser and server.
Summary
In conclusion, RxDB is a powerful and feature-rich solution for browser-based storage. Its adaptability, real-time capabilities, TypeScript support, and optimization for JavaScript applications make it an ideal choice for modern web development projects, addressing the limitations of traditional SQL databases in the browser. Developers can harness RxDB to create efficient, responsive, and user-friendly web applications that leverage the full potential of browser storage.
Follow Up
To explore more about RxDB and leverage its capabilities for browser storage, check out the following resources:
- RxDB GitHub Repository: Visit the official GitHub repository of RxDB to access the source code, documentation, and community support.
- RxDB Quickstart: Get started quickly with RxDB by following the provided quickstart guide, which provides step-by-step instructions for setting up and using RxDB in your projects.
 Ask a question on the forums about Browser Storage - RxDB...
Ask a question on the forums about Browser Storage - RxDB...