IndexedDB Database in Vue Apps - The Power of RxDB
Building robust, offline-capable Vue applications often involves leveraging browser storage solutions to manage data. IndexedDB is one such powerful tool, but its raw API can be challenging to work with directly. RxDB abstracts away much of IndexedDB's complexity, providing a more developer-friendly experience. In this article, we'll explore what IndexedDB is, why it's beneficial in Vue applications, the challenges of using plain IndexedDB, and how RxDB can simplify your development process while adding advanced features.
What is IndexedDB?
IndexedDB is a low-level API for storing significant amounts of structured data in the browser. It provides a transactional database system that can store key-value pairs, complex objects, and more. This storage engine is asynchronous and supports advanced data types, making it suitable for offline storage and complex web applications.
Why Use IndexedDB in Vue
When building Vue applications, IndexedDB can play a crucial role in enhancing both performance and user experience. Here are some reasons to consider using IndexedDB:
- Offline-First / Local-First: By storing data locally, your application remains functional even without an internet connection.
- Performance: Using local data means zero latency and no loading spinners, as data doesn't need to be fetched over a network.
- Easier Implementation: Replicating all data to the client once is often simpler than implementing multiple endpoints for each user interaction.
- Scalability: Local data reduces server load because queries run on the client side, decreasing server bandwidth and processing requirements.
Why To Not Use Plain IndexedDB
While IndexedDB itself is powerful, its native API comes with several drawbacks for everyday application developers:
- Callback-Based API: IndexedDB was originally designed around callbacks rather than modern Promises, making asynchronous code more cumbersome.
- Complexity: IndexedDB is low-level, intended for library developers rather than for app developers who just want to store and query data easily.
- Basic Query API: Its rudimentary query capabilities limit how you can efficiently perform complex queries. Libraries like RxDB offer more advanced querying and indexing.
- TypeScript Support: Ensuring good TypeScript support with IndexedDB is challenging, especially when trying to maintain schema consistency.
- Lack of Observable API: IndexedDB doesn't provide an observable API out of the box, making it hard to automatically update your Vue app in real time. RxDB solves this by enabling you to observe queries or specific documents.
- Cross-Tab Communication: Managing cross-tab updates in plain IndexedDB is difficult. RxDB handles this seamlessly - changes in one tab automatically affect observed data in others.
- Missing Advanced Features: Features like encryption or compression aren't built into IndexedDB, but they are available via RxDB.
- Limited Platform Support: IndexedDB is browser-only. RxDB offers swappable storages so you can reuse the same data layer code in mobile or desktop environments.
Set up RxDB in Vue
Setting up RxDB with Vue is straightforward. It abstracts IndexedDB complexities and adds a layer of powerful features over it.
Installing RxDB
First, install RxDB (and RxJS) from npm:
npm install rxdb rxjs --saveCreate a Database and Collections
RxDB provides two main storage options:
- The free LocalStorage-based storage
- The premium plain IndexedDB-based storage, offering faster performance
Below is an example of setting up a simple RxDB database using the localstorage-based storage in a Vue app:
// db.ts
import { createRxDatabase } from 'rxdb';
import { getRxStorageLocalstorage } from 'rxdb/plugins/storage-localstorage';
export async function initDB() {
const db = await createRxDatabase({
name: 'heroesdb', // the name of the database
storage: getRxStorageLocalstorage()
});
// Define your schema
const heroSchema = {
title: 'hero schema',
version: 0,
description: 'Describes a hero in your app',
primaryKey: 'id',
type: 'object',
properties: {
id: {
type: 'string',
maxLength: 100
},
name: {
type: 'string'
},
power: {
type: 'string'
}
},
required: ['id', 'name']
};
// add collections
await db.addCollections({
heroes: {
schema: heroSchema
}
});
return db;
}CRUD Operations
Once your database is initialized, you can perform all CRUD operations:
// insert
await db.heroes.insert({ id: '1', name: 'Iron Man', power: 'Genius-level intellect' });
// bulk insert
await db.heroes.bulkInsert([
{ id: '2', name: 'Thor', power: 'God of Thunder' },
{ id: '3', name: 'Hulk', power: 'Superhuman Strength' }
]);
// find and findOne
const heroes = await db.heroes.find().exec();
const ironMan = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Iron Man' } }).exec();
// update
const doc = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Hulk' } }).exec();
await doc.update({ $set: { power: 'Unlimited Strength' } });
// delete
const thorDoc = await db.heroes.findOne({ selector: { name: 'Thor' } }).exec();
await thorDoc.remove();Reactive Queries and Live Updates
RxDB excels in providing reactive data capabilities, ideal for real-time applications. Subscribing to queries automatically updates your Vue components when underlying data changes - even across browser tabs.
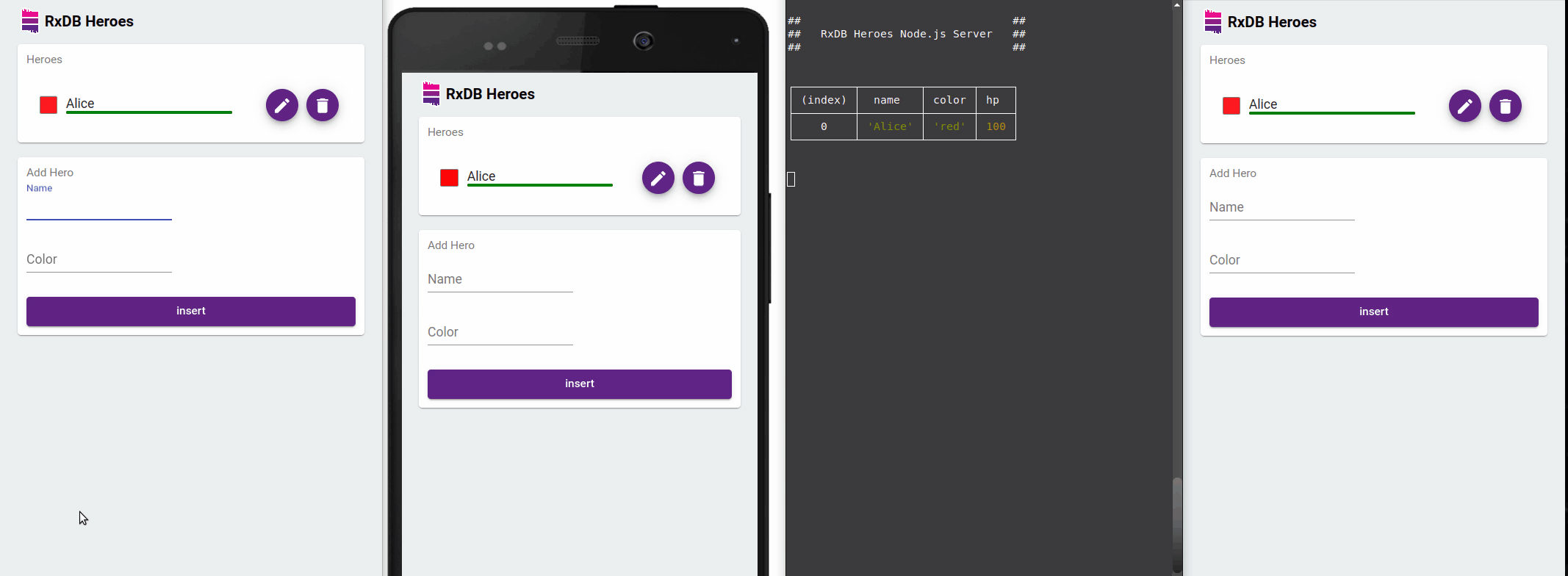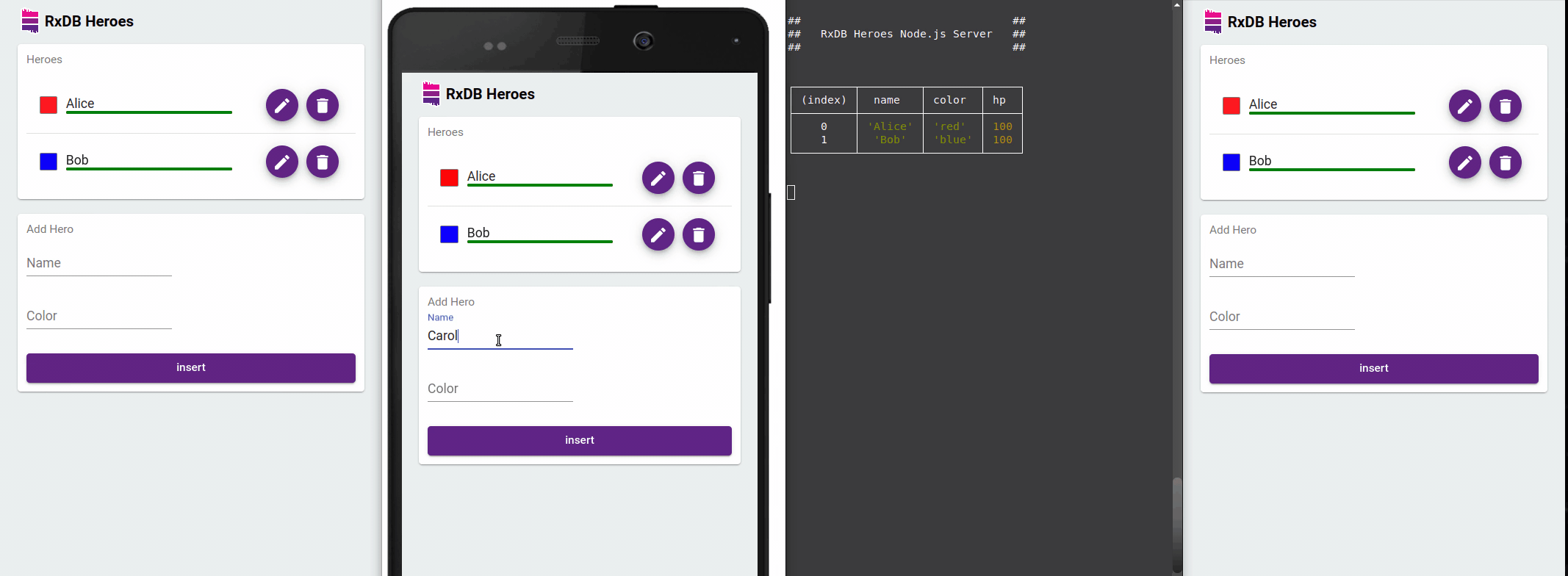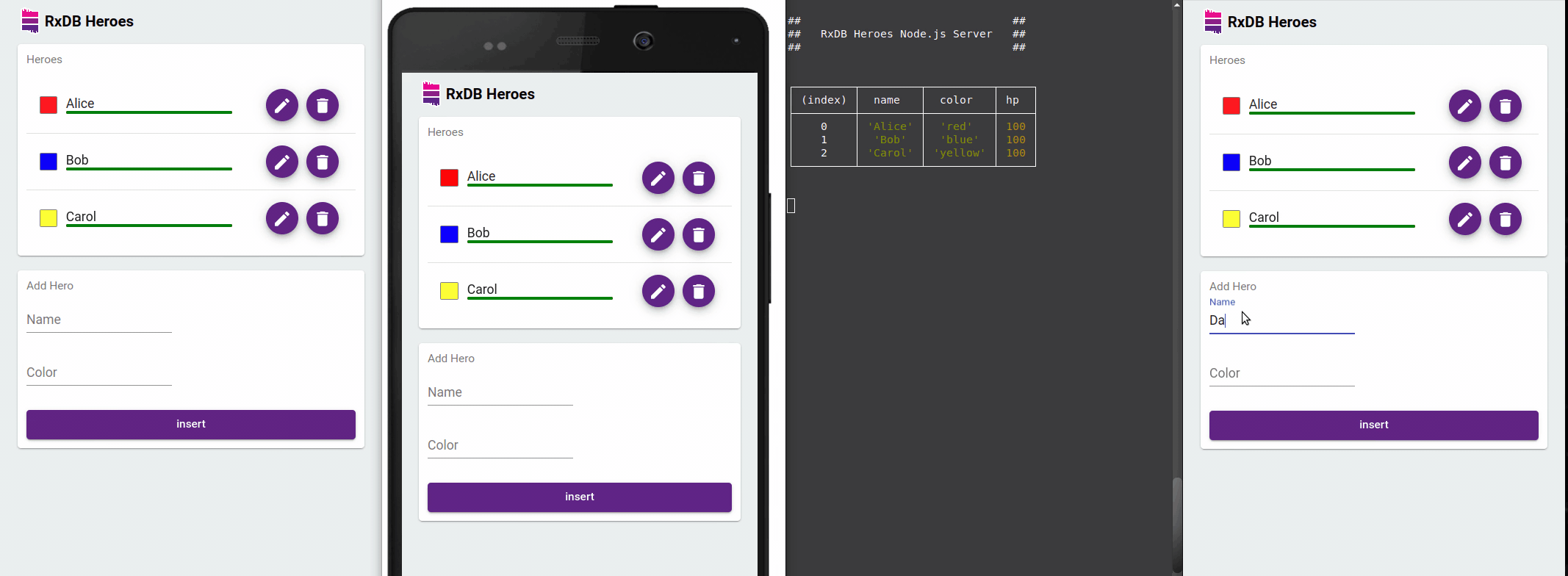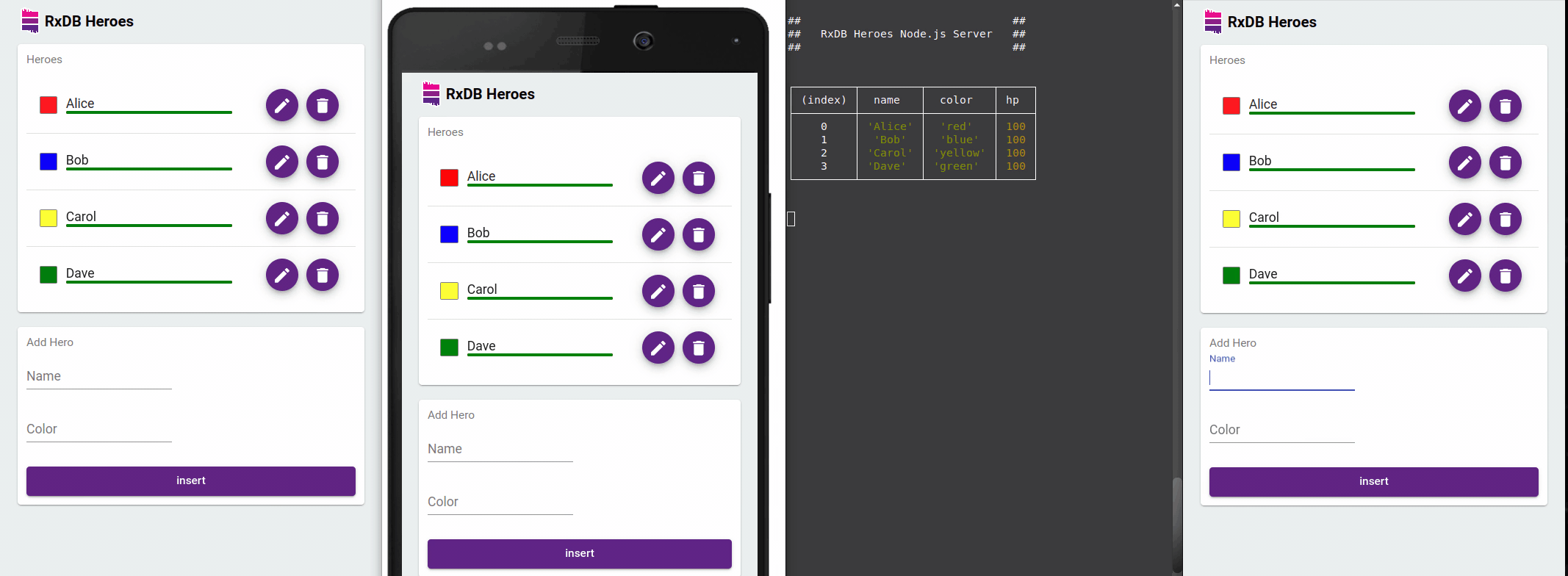
Using RxJS Observables with Vue 3 Composition API
Here's an example of a Vue component that subscribes to live data updates:
<template>
<div>
<h2>Hero List</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="hero in heroes" :key="hero.id">
<strong>{{ hero.name }}</strong> - {{ hero.power }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue';
import { initDB } from '@/db';
const heroes = ref<any[]>([]);
onMounted(async () => {
const db = await initDB();
// create an observable query
const query = db.heroes.find();
// subscribe to the query
query.$.subscribe((newHeroes: any[]) => {
heroes.value = newHeroes;
});
});
</script>This component subscribes to the collection's changes, updating the UI automatically whenever the underlying data changes in any browser tab.
Using Vue Signals
If you're exploring Vue's reactivity transforms or signals, RxDB also offers custom reactivity factories (premium plugins are required). This allows queries to emit data as signals instead of traditional Observables.
const heroesSignal = db.heroes.find().$$; // $$ indicates a reactive result
With this, in your Vue template or script, you can directly read from heroesSignal()
<template>
<div>
<h2>Hero List</h2>
<ul>
<!-- we read heroesSignal.value which is always up to date -->
<li v-for="hero in heroesSignal.value" :key="hero.id">
<strong>{{ hero.name }}</strong> - {{ hero.power }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>Vue IndexedDB Example with RxDB
A comprehensive example of using RxDB within a Vue application can be found in the RxDB GitHub repository. This repository contains sample applications, showcasing best practices and demonstrating how to integrate RxDB for various use cases.
Advanced RxDB Features
RxDB offers many advanced features that extend beyond basic data storage:
-
RxDB Replication: Synchronize local data with remote databases seamlessly.
-
Data Migration: Handle schema changes gracefully with automatic data migrations.
-
Encryption: Secure your data with built-in encryption capabilities.
-
Compression: Optimize storage using key compression.
Limitations of IndexedDB
While IndexedDB is powerful, it has some inherent limitations:
- Performance: IndexedDB can be slow under certain conditions. Read more: Slow IndexedDB
- Storage Limits: Browsers impose limits on how much data can be stored. See: Browser storage limits.
Alternatives to IndexedDB
Depending on your application's requirements, there are alternative storage solutions to consider:
- Origin Private File System (OPFS): A newer API that can offer better performance. RxDB supports OPFS as well. More info: RxDB OPFS Storage
- SQLite: Ideal for hybrid frameworks or Capacitor, offering native performance. Explore: RxDB SQLite Storage
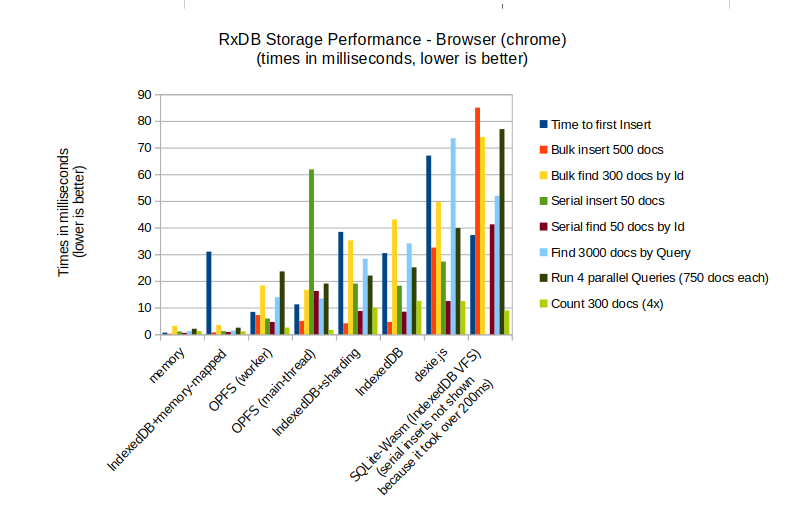
Performance Comparison with Other Browser Storages
Here is a performance overview of the various browser-based storage implementations of RxDB:
Follow Up
- Learn how to use RxDB with the RxDB Quickstart for a guided introduction.
- Check out the RxDB GitHub repository and leave a star ⭐ if you find it useful.
By leveraging RxDB on top of IndexedDB, you can create highly responsive, offline-capable Vue applications without dealing with the low-level complexities of IndexedDB directly. With reactive queries, seamless cross-tab communication, and powerful advanced features, RxDB becomes an invaluable tool in modern web development.
 Ask a question on the forums about IndexedDB Database in...
Ask a question on the forums about IndexedDB Database in...